Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase catalyzed reactions in D2O: product release limits the rate of this sluggish enzyme-catalyzed reaction
- PMID: 22471428
- PMCID: PMC3334862
- DOI: 10.1021/ja302154k
Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase catalyzed reactions in D2O: product release limits the rate of this sluggish enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Abstract
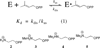
The E. coli isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase (IDI) catalyzed reaction of isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) in D(2)O gives a 66% yield of dimethylallyl diphosphate labeled with deuterium at the (E)-methyl group (d-DMAPP) and a 34% yield of IPP labeled with 1 mol of deuterium at C-2 (d-IPP). This shows that the release to D(2)O of the initial product of the IDI-catalyzed reaction (d-DMAPP) is slower than its conversion to d-IPP. Product dissociation is therefore rate determining for isomerization of IPP with a rate constant k(dis) ≈ k(cat) = 0.08 s(-1). The data provide an estimated rate constant of k(as) = 6 × 10(3) M(-1) s(-1) for binding of DMAPP to E. coli IDI that is similar to rate constants determined for the binding of N-protonated 2-amino ethyl diphosphate intermediate analogs to IDI from yeast [Reardon, J. E.; Abeles, R. H. Biochemistry1986, 25, 5609-5616]. We propose that ligand binding to IDI is relatively slow because there is a significant kinetic barrier to reorganization of the initial encounter complex between enzyme, substrate, and an essential Mg(2+) to form the Michaelis complex where the metal cation bridges the protein and the substrate diphosphate group.
© 2012 American Chemical Society
Figures



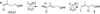

Similar articles
-
Mechanistic Studies of the Protonation-Deprotonation Reactions for Type 1 and Type 2 Isopentenyl Diphosphate:Dimethylallyl Diphosphate Isomerase.J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Oct 10;140(40):12900-12908. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b07274. Epub 2018 Sep 25. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 30183274
-
Kinetic and Binding Studies of Streptococcus pneumoniae Type 2 Isopentenyl Diphosphate:Dimethylallyl Diphosphate Isomerase.Biochemistry. 2016 Apr 19;55(15):2260-8. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00087. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27003727
-
Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase. Mechanism-based inhibition by diene analogues of isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate.J Am Chem Soc. 2005 Dec 14;127(49):17433-8. doi: 10.1021/ja056187h. J Am Chem Soc. 2005. PMID: 16332094 Free PMC article.
-
The type II isopentenyl Diphosphate:Dimethylallyl diphosphate isomerase (IDI-2): A model for acid/base chemistry in flavoenzyme catalysis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Oct 15;632:47-58. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.05.017. Epub 2017 May 31. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28577910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversity of the biosynthesis of the isoprene units.Nat Prod Rep. 2003 Apr;20(2):171-83. doi: 10.1039/b109860h. Nat Prod Rep. 2003. PMID: 12735695 Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering the Role of Key Active-Site Side Chains in Catalysis: An Extended Brønsted Relationship for Substrate Deprotonation Catalyzed by Wild-Type and Variants of Triosephosphate Isomerase.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 Oct 9;141(40):16139-16150. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b08713. Epub 2019 Sep 25. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 31508957 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase involved in the juvenile hormone pathway in Aedes aegypti.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 Oct;42(10):751-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22782071 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Deuterium Kinetic Isotope Effects: A Probe for the Origin of the Rate Acceleration for Hydride Transfer Catalyzed by Glycerol-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase.Biochemistry. 2018 Jul 24;57(29):4338-4348. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00536. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29927590 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway for microbial terpenoid production through metabolic control analysis.Microb Cell Fact. 2019 Nov 5;18(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12934-019-1235-5. Microb Cell Fact. 2019. PMID: 31690314 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis of grapevine in response to copper stress.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 17;5:17749. doi: 10.1038/srep17749. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26673527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agranoff BW, Eggerer H, Henning U, Lynen F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1959;81:1254–1255.
-
- Reardon JE, Abeles RH. Biochemistry. 1986;25:5609–5616. - PubMed
-
- Muehlbacher M, Poulter CD. Biochemistry. 1988;27:7315–7328. - PubMed
-
- Kuzuyama T, Seto H. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2003;20:171–183. - PubMed
-
- Toteva MM, Richard JP. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996;118:11434–11445.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

