Crystal structure of an HIV-binding recombinant fragment of human CD4
- PMID: 2247146
- PMCID: PMC5638305
- DOI: 10.1038/348419a0
Crystal structure of an HIV-binding recombinant fragment of human CD4
Abstract
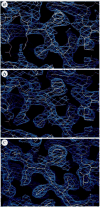
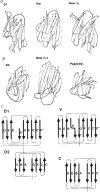
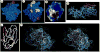
CD4 glycoprotein on the surface of T cells helps in the immune response and is the receptor for HIV infection. The structure of a soluble fragment of CD4 determined at 2.3 A resolution reveals that the molecule has two intimately associated immunoglobulin-like domains. Residues implicated in HIV recognition by analysis of mutants and antibody binding are salient features in domain D1. Domain D2 is distinguished by a variation on the beta-strand topologies of antibody domains and by an intra-sheet disulphide bridge.
Figures


Comment in
-
Immunology. One hand clapping.Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):393-4. doi: 10.1038/348393a0. Nature. 1990. PMID: 2247144 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

