Role of carotenoid β-cryptoxanthin in bone homeostasis
- PMID: 22471523
- PMCID: PMC3361488
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-36
Role of carotenoid β-cryptoxanthin in bone homeostasis
Abstract
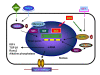
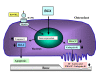
Bone homeostasis is maintained through a balance between osteoblastic bone formation and osteoclastic bone resorption. Aging induces bone loss due to decreased osteoblastic bone formation and increased osteoclastic bone resorption. Osteoporosis with its accompanying decrease in bone mass is widely recognized as a major public health problem. Nutritional factors may play a role in the prevention of bone loss with aging. Among various carotenoids (carotene and xanthophylls including beta (β)-cryptoxanthin, lutein, lycopene, β-carotene, astaxanthin, and rutin), β-cryptoxanthin, which is abundant in Satsuma mandarin orange (Citrus unshiu MARC.), has been found to have a stimulatory effect on bone calcification in vitro. β-cryptoxanthin has stimulatory effects on osteoblastic bone formation and inhibitory effects on osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro, thereby increasing bone mass. β-cryptoxanthin has an effect on the gene expression of various proteins that are related osteoblastic bone formation and osteoclastic bone resororption in vitro. The intake of β-cryptoxanthin may have a preventive effect on bone loss in animal models for osteoporosis and in healthy human or postmenopausal women. Epidemiological studies suggest a potential role of β-cryptoxanthin as a sustainable nutritional approach to improving bone health of human subjects. β-Cryptoxanthin may be an osteogenic factor in preventing osteoporosis in human subjects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory mechanism of food factors in bone metabolism and prevention of osteoporosis.Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006 Nov;126(11):1117-37. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.126.1117. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006. PMID: 17077614 Review.
-
Nutritional factors and bone homeostasis: synergistic effect with zinc and genistein in osteogenesis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Jul;366(1-2):201-21. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1298-7. Epub 2012 Apr 5. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22476903 Review.
-
beta-Cryptoxanthin stimulates bone formation and inhibits bone resorption in tissue culture in vitro.Mol Cell Biochem. 2004 Mar;258(1-2):137-44. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000012848.50541.19. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15030178
-
The bone anabolic carotenoid beta-cryptoxanthin enhances transforming growth factor-beta1-induced SMAD activation in MC3T3 preosteoblasts.Int J Mol Med. 2009 Nov;24(5):671-5. doi: 10.3892/ijmm_00000278. Int J Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19787201
-
Oral administration of beta-cryptoxanthin prevents bone loss in ovariectomized rats.Int J Mol Med. 2006 Jan;17(1):15-20. Int J Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16328006
Cited by
-
Role of vitamins beyond vitamin D3 in bone health and osteoporosis (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Jan;53(1):9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5333. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38063255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in Plasma Carotenoid Concentrations during the AntioxObesity Weight Reduction Program among Adults with Excessive Body Weight.Nutrients. 2023 Nov 23;15(23):4890. doi: 10.3390/nu15234890. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38068747 Free PMC article.
-
Quali-Quantitative Profile of Native Carotenoids in Kumquat from Brazil by HPLC-DAD-APCI/MS.Foods. 2019 May 16;8(5):166. doi: 10.3390/foods8050166. Foods. 2019. PMID: 31100882 Free PMC article.
-
Methanol Extract of Euchelus asper Prevents Bone Resorption in Ovariectomised Mice Model.J Osteoporos. 2014;2014:348189. doi: 10.1155/2014/348189. Epub 2014 Jun 5. J Osteoporos. 2014. PMID: 24995144 Free PMC article.
-
β-Carotene: a natural osteogen to fabricate osteoinductive electrospun scaffolds.RSC Adv. 2018 Mar 12;8(18):9941-9945. doi: 10.1039/c7ra13237a. eCollection 2018 Mar 5. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35540852 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

