Role of the N-terminus in determining metal-specific responses in the E. coli Ni- and Co-responsive metalloregulator, RcnR
- PMID: 22471551
- PMCID: PMC3375346
- DOI: 10.1021/ja300834b
Role of the N-terminus in determining metal-specific responses in the E. coli Ni- and Co-responsive metalloregulator, RcnR
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Role of the N-terminus in Determining Metal-Specific Responses in the E. coli Ni- and Co-Responsive Metalloregulator, RcnR".J Am Chem Soc. 2017 May 17;139(19):6778. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b04150. Epub 2017 May 4. J Am Chem Soc. 2017. PMID: 28471187 No abstract available.
Abstract
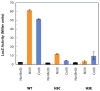
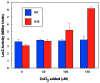
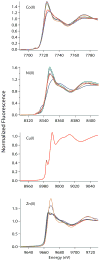
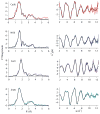
RcnR (resistance to cobalt and nickel regulator) is a 40-kDa homotetrameric protein and metalloregulator that controls the transcription of the Co(II) and Ni(II) exporter, RcnAB, by binding to DNA as an apoprotein and releasing DNA in response to specifically binding Co(II) and Ni(II) ions. Using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) to examine the structure of metals bound and lacZ reporter assays of the transcription of RcnA in response to metal binding, in WT and mutant proteins, the roles of coordination number, ligand selection, and residues in the N-terminus of the protein were examined as determinants in metal ion recognition. The studies show that the cognate metal ions, Co(II) and Ni(II), which bind in (N/O)(5)S six-coordinate sites, are distinguished from non-cognate metal ions (Cu(I) and Zn(II)), which bind only three protein ligands and one anion from the buffer, by coordination number and ligand selection. Using mutations of residues near the N-terminus, the N-terminal amine is shown to be a ligand of the cognate metal ions that is missing in the complexes with non-cognate metal ions. The side chain of His3 is also shown to play an important role in distinguishing metal ions. The imidazole group is shown to be a ligand in the Co(II) RcnR complex, but not in the Zn(II) complex. Further, His3 does not appear to bind to Ni(II), providing a structural basis for the differential regulation of RcnAB by the two cognate ions. The Zn(II) complexes change coordination number in response to the residue in position three. In H3C-RcnR, the Zn(II) complex is five-coordinate, and in H3E-RcnR the Zn(II) ion is bound to six protein ligands. The metric parameters of this unusual Zn(II) structure resemble those of the WT-Ni(II) complex, and the mutant protein is able to regulate expression of RcnAB in response to binding the non-cognate ion. The results are discussed within a protein allosteric model for gene regulation by metalloregulators.
Figures
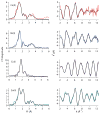
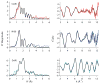
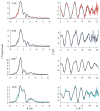
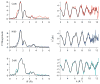
Similar articles
-
Effects of select histidine to cysteine mutations on transcriptional regulation by Escherichia coli RcnR.Biochemistry. 2013 Jan 8;52(1):84-97. doi: 10.1021/bi300886q. Epub 2012 Dec 24. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23215580 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate Ligation in the Ni(II)- and Co(II)-Responsive Escherichia coli Transcriptional Regulator, RcnR.Inorg Chem. 2017 Jun 5;56(11):6459-6476. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b00527. Epub 2017 May 18. Inorg Chem. 2017. PMID: 28517938 Free PMC article.
-
Ni(II) Sensing by RcnR Does Not Require an FrmR-Like Intersubunit Linkage.Inorg Chem. 2019 Oct 21;58(20):13639-13653. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01096. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Inorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31247878
-
Coordinating intracellular nickel-metal-site structure-function relationships and the NikR and RcnR repressors.Nat Prod Rep. 2010 May;27(5):658-67. doi: 10.1039/b906683g. Epub 2010 Mar 5. Nat Prod Rep. 2010. PMID: 20442957 Review.
-
The SmtB/ArsR family of metalloregulatory transcriptional repressors: Structural insights into prokaryotic metal resistance.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2003 Jun;27(2-3):131-43. doi: 10.1016/S0168-6445(03)00054-8. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12829264 Review.
Cited by
-
Metal specificity of cyanobacterial nickel-responsive repressor InrS: cells maintain zinc and copper below the detection threshold for InrS.Mol Microbiol. 2014 May;92(4):797-812. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12594. Epub 2014 Apr 14. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24666373 Free PMC article.
-
The Electronic Structure of the Metal Active Site Determines the Geometric Structure and Function of the Metalloregulator NikR.Biochemistry. 2019 Aug 27;58(34):3585-3591. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00542. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31339709 Free PMC article.
-
Nickel Ligation of the N-Terminal Amine of HypA Is Required for Urease Maturation in Helicobacter pylori.Biochemistry. 2017 Feb 28;56(8):1105-1116. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00912. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28177601 Free PMC article.
-
Metallochaperones and metalloregulation in bacteria.Essays Biochem. 2017 May 9;61(2):177-200. doi: 10.1042/EBC20160076. Print 2017 May 9. Essays Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28487396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generating a Metal-responsive Transcriptional Regulator to Test What Confers Metal Sensing in Cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 7;290(32):19806-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.663427. Epub 2015 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26109070 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

