Depletion of OLFM4 gene inhibits cell growth and increases sensitization to hydrogen peroxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced-apoptosis in gastric cancer cells
- PMID: 22471589
- PMCID: PMC3359197
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-38
Depletion of OLFM4 gene inhibits cell growth and increases sensitization to hydrogen peroxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced-apoptosis in gastric cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Human olfactomedin 4 (OLFM4) gene is a secreted glycoprotein more commonly known as the anti-apoptotic molecule GW112. OLFM4 is found to be frequently up-regulated in many types of human tumors including gastric cancer and it was believed to play significant role in the progression of gastric cancer. Although the function of OLFM4 has been indicated in many studies, recent evidence strongly suggests a cell or tissue type-dependent role of OLFM4 in cell growth and apoptosis. The aim of this study is to examine the role of gastric cancer-specific expression of OLFM4 in cell growth and apoptosis resistance.
Methods: OLFM4 expression was eliminated by RNA interference in SGC-7901 and MKN45 cells. Cell proliferation, anchorage-independent growth, cell cycle and apoptosis were characterized in vitro. Tumorigenicity was analyzed in vivo. The apoptosis and caspase-3 activation in response to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF α) were assessed in the presence or absence of caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-fmk.
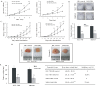
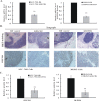
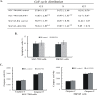
Results: The elimination of OLFM4 protein by RNA interference in SGC-7901 and MKN45 cells significantly inhibits tumorigenicity both in vitro and in vivo by induction of cell G1 arrest (all P < 0.01). OLFM4 knockdown did not trigger obvious cell apoptosis but increased H2O2 or TNF α-induced apoptosis and caspase-3 activity (all P < 0.01). Treatment of Z-VAD-fmk attenuated caspase-3 activity and significantly reversed the H(2)O(2) or TNF α-induced apoptosis in OLFM4 knockdown cells (all P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Our study suggests that depletion of OLFM4 significantly inhibits tumorigenicity of the gastric cancer SGC-7901 and MKN45 cells. Blocking OLFM4 expression can sensitize gastric cancer cells to H2O2 or TNF α treatment by increasing caspase-3 dependent apoptosis. A combination strategy based on OLFM4 inhibition and anticancer drugs treatment may provide therapeutic potential in gastric cancer intervention.
Figures

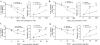
Similar articles
-
Olfactomedin-4 in digestive diseases: A mini-review.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 May 7;24(17):1881-1887. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1881. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29740203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olfactomedin 4 promotes gastric cancer cell G2/M progression and serves as a therapeutic target in gastric adenocarcinoma.Carcinogenesis. 2025 Apr 3;46(2):bgaf010. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgaf010. Carcinogenesis. 2025. PMID: 40056162
-
z-VAD-fmk augmentation of TNF alpha-stimulated neutrophil apoptosis is compound specific and does not involve the generation of reactive oxygen species.Blood. 2005 Apr 1;105(7):2970-2. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2870. Epub 2004 Nov 30. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15572588
-
Bax cleavage implicates caspase-dependent H2O2-induced apoptosis of hepatocytes.Int J Mol Med. 2003 Mar;11(3):369-74. Int J Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 12579342
-
Olfactomedin 4 Is a Biomarker for the Severity of Infectious Diseases.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022 Feb 8;9(4):ofac061. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac061. eCollection 2022 Apr. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35291445 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergy and Antagonism of Active Constituents of ADAPT-232 on Transcriptional Level of Metabolic Regulation of Isolated Neuroglial Cells.Front Neurosci. 2013 Feb 20;7:16. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00016. eCollection 2013. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23430930 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of OLFM4 with the Progression and Cisplatin Resistance of Head and Neck Squamous Carcinoma.Curr Oncol. 2025 May 13;32(5):276. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32050276. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40422535 Free PMC article.
-
OLFM4 Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastatic Potential of Cervical Cancer Cells.Oncol Res. 2019 Jul 12;27(7):763-771. doi: 10.3727/096504018X15399955297355. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 30764901 Free PMC article.
-
Ligands for glaucoma-associated myocilin discovered by a generic binding assay.ACS Chem Biol. 2014 Feb 21;9(2):517-25. doi: 10.1021/cb4007776. Epub 2013 Dec 9. ACS Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24279319 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactomedin-4 in digestive diseases: A mini-review.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 May 7;24(17):1881-1887. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1881. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29740203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

