Prevalence of collagen VII-specific autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune and inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 22471736
- PMCID: PMC3368718
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-13-16
Prevalence of collagen VII-specific autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune and inflammatory diseases
Abstract
Background: Autoimmunity to collagen VII is typically associated with the skin blistering disease epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA), but also occurs occasionally in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus or inflammatory bowel disease. The aim of our present study was to develop an accurate immunoassay for assessing the presence of autoantibodies against collagen VII in large cohorts of patients and healthy donors.
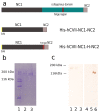
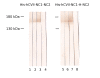
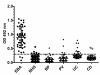
Methods: Based on in silico antigenic analysis and previous wetlab epitope mapping data, we designed a chimeric collagen VII construct containing all collagen VII epitopes with higher antigenicity. ELISA was performed with sera from patients with EBA (n = 50), Crohn's disease (CD, n = 50), ulcerative colitis (UC, n = 50), bullous pemphigoid (BP, n = 76), and pemphigus vulgaris (PV, n = 42) and healthy donors (n = 245).
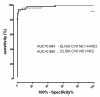
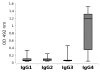
Results: By ELISA, the receiver operating characteristics analysis yielded an area under the curve of 0.98 (95% CI: 0.9638-1.005), allowing to set the cut-off at 0.32 OD at a calculated specificity of 98% and a sensitivity of 94%. Running the optimized test showed that serum IgG autoantibodies from 47 EBA (94%; 95% CI: 87.41%-100%), 2 CD (4%; 95% CI: 0%-9.43%), 8 UC (16%; 95% CI: 5.8%-26%), 2 BP (2.63%; 95% CI: 0%-6.23%), and 4 PV (9.52%; 95% CI: 0%-18.4%) patients as well as from 4 (1.63%; 95% CI: 0%-3.21%) healthy donors reacted with the chimeric protein. Further analysis revealed that in 34%, 37%, 16% and 100% of sera autoantibodies of IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 isotype, respectively, recognized the recombinant autoantigen.
Conclusions: Using a chimeric protein, we developed a new sensitive and specific ELISA to detect collagen specific antibodies. Our results show a low prevalence of collagen VII-specific autoantibodies in inflammatory bowel disease, pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. Furthermore, we show that the autoimmune response against collagen VII is dominated by IgG4 autoantibodies. The new immunoassay should prove a useful tool for clinical and translational research and should improve the routine diagnosis and disease monitoring in diseases associated with collagen VII-specific autoimmunity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sensitive and specific assays for routine serological diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Mar;68(3):e89-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2011.12.032. Epub 2012 Feb 16. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 22341608
-
Diagnosis and disease severity assessment of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita by ELISA for anti-type VII collagen autoantibodies: an Italian multicentre study.Br J Dermatol. 2013 Jan;168(1):80-4. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12011. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Br J Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 22913489
-
Serum levels of anti-type VII collagen antibodies detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in patients with epidermolysis bullosa acquisita are correlated with the severity of skin lesions.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013 Feb;27(2):e224-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04617.x. Epub 2012 Jun 25. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013. PMID: 22731917
-
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: what's new?J Dermatol. 2010 Mar;37(3):220-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00799.x. J Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20507385 Review.
-
Clinical features and diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017 Feb;13(2):157-169. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2016.1221343. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27580464 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of Acquired Autoimmune Blistering Diseases in Inherited Epidermolysis Bullosa: Implications for the Future of Gene Therapy.Antibodies (Basel). 2021 May 17;10(2):19. doi: 10.3390/antib10020019. Antibodies (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bullous pemphigoid and mucous membrane pemphigoid humoral responses differ in reactivity towards BP180 midportion and BP230.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 29;15:1494294. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1494294. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39676877 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical relevance of autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune bullous dermatosis.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:369546. doi: 10.1155/2012/369546. Epub 2012 Dec 24. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23320017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blister-inducing antibodies target multiple epitopes on collagen VII in mice.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Sep;18(9):1727-39. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12338. Epub 2014 Aug 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 25091020 Free PMC article.
-
Autoimmune Subepidermal Bullous Diseases of the Skin and Mucosae: Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Management.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Feb;54(1):26-51. doi: 10.1007/s12016-017-8633-4. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28779299 Review.
References
-
- Woodley DT, Briggaman RA, O'Keefe EJ, Inman AO, Queen LL, Gammon WR. Identification of the skin basement-membrane autoantigen in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. N Engl J Med. 1984;310:1007–1013. - PubMed
-
- Gammon WR, Fine JD, Forbes M, Briggaman RA. Immunofluorescence on split skin for the detection and differentiation of basement membrane zone autoantibodies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:79–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

