The Framingham Brain Donation Program: neuropathology along the cognitive continuum
- PMID: 22471865
- PMCID: PMC3622706
- DOI: 10.2174/156720512801322609
The Framingham Brain Donation Program: neuropathology along the cognitive continuum
Abstract
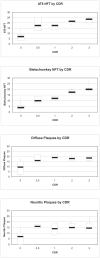
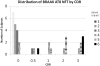
The Framingham Heart Study has enrolled 3 generations of participants, the original cohort (gen 1) enrolled in 1948, the offspring cohort (gen 2) enrolled in 1971 and the third generation enrolled in 2002. Participants have been undergoing prospective surveillance for incident stroke and dementia and embedded within this cohort is the voluntary Framingham Brain Donation Program that was begun in 1997. Participants who register to become brain donors have had one or more brain MR and cognitive test batteries administered. In addition, they undergo neurological evaluation as indicated, record review and post-mortem next-of-kin interview to determine the presence, type and extent of antemortem, clinical neurological diagnoses and to assign a retrospective clinical dementia rating (CDR) Scale score. Between 1997 and 2009 there were 1806 deaths, 186 of which were among registered brain donors and of these 139 brains could be examined. 58% were deemed cognitively normal at death. We present results for 3 projects; the first was to examine the sensitivity and specificity of our clinical diagnosis against the gold standard of pathological AD in 59 persons who underwent detailed cognitive assessment in the two years prior to death; we observed a 77.3% sensitivity (2 persons with AD were diagnosed clinically as Lewy body dementia) and a 91.9% specificity. The second examined the correlation of regional Alzheimer-type pathology to cognitive status at death among 34 persons who were over the age of 75 and without any significant vascular or alternative neurodegenerative pathology and found that neurofibrillary tangle counts distinguished between persons who were controls, had mild cognitive impairment, mild or moderate dementia; tangles in dorsolateral frontal cortex best distinguished MCI and controls. The third project examined the extent and severity of vascular pathology, again in a larger sample of varying cognitive abilities and in a subsample of persons with either amnestic or nonamnestic MCI. We observed that an aggregate ischemic injury score was significantly higher in persons with a CDR score of 0.5 than in normal controls.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Dawber TR, Kannel WB. The Framingham study. An epidemiological approach to coronary heart disease. Circulation. 1966;34:553–555. - PubMed
-
- Feinleib M, Kannel WB, Garrison RJ, McNamara PM, Castelli WP. The Framingham Offspring Study. Design and preliminary data. Prev Med. 1975;4:518–525. - PubMed
-
- Splansky GL, Corey D, Yang Q, Atwood LD, Cupples LA, Benjamin EJ, et al. The Third Generation Cohort of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Framingham Heart Study: design, recruitment, and initial examination. Am J Epidemiol. 2007;165:1328–1335. - PubMed
-
- Bachman DL, Wolf PA, Linn R, Knoefel JE, Cobb J, Belanger A, et al. Prevalence of dementia and probable senile dementia of the Alzheimer type in the Framingham Study. Neurology. 1992;42(1):115–9. - PubMed
-
- Bachman DL, Wolf PA, Linn RT, Knoefel JE, Cobb JL, Belanger AJ, et al. Incidence of dementia and probable Alzheimer's disease in a general population: the Framingham Study. Neurology. 1993;43(3 Pt 1):515–9. - PubMed