Ginsenoside-Rp1 inhibits platelet activation and thrombus formation via impaired glycoprotein VI signalling pathway, tyrosine phosphorylation and MAPK activation
- PMID: 22471932
- PMCID: PMC3448917
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01967.x
Ginsenoside-Rp1 inhibits platelet activation and thrombus formation via impaired glycoprotein VI signalling pathway, tyrosine phosphorylation and MAPK activation
Abstract
Background and purpose: Ginsenosides are the main constituents for the pharmacological effects of Panax ginseng. Such effects of ginsenosides including cardioprotective and anti-platelet activities have shown stability and bioavailability limitations. However, information on the anti-platelet activity of ginsenoside-Rp1 (G-Rp1), a stable derivative of ginsenoside-Rg3, is scarce. We examined the ability of G-Rp1 to modulate agonist-induced platelet activation.
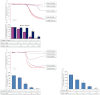
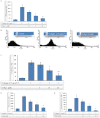
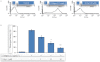
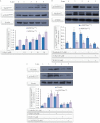
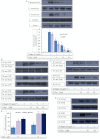
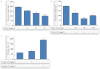
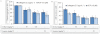
Experimental approach: G-Rp1 in vitro and ex vivo effects on agonist-induced platelet-aggregation, granule-secretion, [Ca(2+) ](i) mobilization, integrin-α(IIb) β(3) activation were examined. Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) and MAPK expressions and levels of tyrosine phosphorylation of the glycoprotein VI (GPVI) signalling pathway components were also studied. G-Rp1 effects on arteriovenous shunt thrombus formation in rats or tail bleeding time and ex vivo coagulation time in mice were determined. KEY RESULT: G-Rp1 markedly inhibited platelet aggregation induced by collagen, thrombin or ADP. While G-Rp1 elevated cAMP levels, it dose-dependently suppressed collagen-induced ATP-release, thromboxane secretion, p-selectin expression, [Ca(2+) ](i) mobilization and α(IIb) β(3) activation and attenuated p38(MAPK) and ERK2 activation. Furthermore, G-Rp1 inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation of multiple components (Fyn, Lyn, Syk, LAT, PI3K and PLCγ2) of the GPVI signalling pathway. G-Rp1 inhibited in vivo thrombus formation and ex vivo platelet aggregation and ATP secretion without affecting tail bleeding time and coagulation time, respectively.
Conclusion and implications: G-Rp1 inhibits collagen-induced platelet activation and thrombus formation through modulation of early GPVI signalling events, and this effect involves VASP stimulation, and ERK2 and p38(-MAPK) inhibition. These data suggest that G-Rp1 may have therapeutic potential for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases involving aberrant platelet activation.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

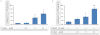

Similar articles
-
Anti-platelet role of Korean ginseng and ginsenosides in cardiovascular diseases.J Ginseng Res. 2020 Jan;44(1):24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.05.005. Epub 2019 May 21. J Ginseng Res. 2020. PMID: 32095094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside-Rp3 inhibits platelet activation and thrombus formation by regulating MAPK and cyclic nucleotide signaling.Vascul Pharmacol. 2018 Oct;109:45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Vascul Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29890296
-
A noble function of BAY 11-7082: Inhibition of platelet aggregation mediated by an elevated cAMP-induced VASP, and decreased ERK2/JNK1 phosphorylations.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Feb 10;627(1-3):85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.11.005. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19913011
-
Gintonin modulates platelet function and inhibits thrombus formation via impaired glycoprotein VI signaling.Platelets. 2019;30(5):589-598. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2018.1479033. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Platelets. 2019. PMID: 29870296
-
Modulation of Glycoprotein VI and Its Downstream Signaling Pathways as an Antiplatelet Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 31;23(17):9882. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179882. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077280 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adaptogenic effects of Panax ginseng on modulation of cardiovascular functions.J Ginseng Res. 2020 Jul;44(4):538-543. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.03.001. Epub 2020 Mar 28. J Ginseng Res. 2020. PMID: 32617033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Panax ginseng: Inflammation, platelet aggregation, thrombus formation, and atherosclerosis crosstalk.J Ginseng Res. 2022 Jan;46(1):54-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.09.003. Epub 2021 Oct 5. J Ginseng Res. 2022. PMID: 35058727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Schizonepeta tenuifolia inhibits collagen stimulated platelet function via suppressing MAPK and Akt signaling.J Biomed Res. 2019 Feb 18;33(4):250-7. doi: 10.7555/JBR.32.20180031. Online ahead of print. J Biomed Res. 2019. PMID: 30783025 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-platelet role of Korean ginseng and ginsenosides in cardiovascular diseases.J Ginseng Res. 2020 Jan;44(1):24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.05.005. Epub 2019 May 21. J Ginseng Res. 2020. PMID: 32095094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ulmus parvifolia Modulates Platelet Functions and Inhibits Thrombus Formation by Regulating Integrin αIIbβ3 and cAMP Signaling.Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 19;11:698. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00698. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32508642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam F, Kauskot A, Rosa J-P, Bryckaert M. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in hemostasis and thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6:2007–2016. - PubMed
-
- Adam F, Kauskot A, Nurden P, Sulpice E, Hoylaerts MF, Davis RJ, et al. Platelet JNK1 is involved in secretion and thrombus formation. Blood. 2010;115:4083–4092. - PubMed
-
- Andrews RK, Berndt MC. Platelet physiology and thrombosis. Thromb Res. 2004;114:447–453. - PubMed
-
- Attele AS, Wu JA, Yuan C-S. Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;58:1685–1693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

