Differential pattern and prognostic significance of CD4+, FOXP3+ and IL-17+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in ductal and lobular breast cancers
- PMID: 22471961
- PMCID: PMC3362763
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-134
Differential pattern and prognostic significance of CD4+, FOXP3+ and IL-17+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in ductal and lobular breast cancers
Abstract
Background: Clinical relevance of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer is controversial. Here, we used a tumor microarray including a large series of ductal and lobular breast cancers with long term follow up data, to analyze clinical impact of TIL expressing specific phenotypes and distribution of TILs within different tumor compartments and in different histological subtypes.
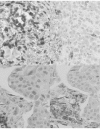
Methods: A tissue microarray (TMA) including 894 ductal and 164 lobular breast cancers was stained with antibodies recognizing CD4, FOXP3, and IL-17 by standard immunohistochemical techniques. Lymphocyte counts were correlated with clinico-pathological parameters and survival.
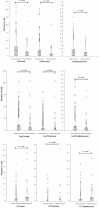
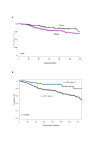
Results: CD4(+) lymphocytes were more prevalent than FOXP3(+) TILs whereas IL-17(+) TILs were rare. Increased numbers of total CD4(+) and FOXP3(+) TIL were observed in ductal, as compared with lobular carcinomas. High grade (G3) and estrogen receptor (ER) negative ductal carcinomas displayed significantly (p < 0.001) higher CD4(+) and FOXP3(+) lymphocyte infiltration while her2/neu over-expression in ductal carcinomas was significantly (p < 0.001) associated with higher FOXP3(+) TIL counts. In contrast, lymphocyte infiltration was not linked to any clinico-pathological parameters in lobular cancers. In univariate but not in multivariate analysis CD4(+) infiltration was associated with significantly shorter survival in patients bearing ductal, but not lobular cancers. However, a FOXP3(+)/CD4(+) ratio > 1 was associated with improved overall survival even in multivariate analysis (p = 0.033).
Conclusions: Ductal and lobular breast cancers appear to be infiltrated by different lymphocyte subpopulations. In ductal cancers increased CD4(+) and FOXP3(+) TIL numbers are associated with more aggressive tumor features. In survival analysis, absolute numbers of TILs do not represent major prognostic indicators in ductal and lobular breast cancer. Remarkably however, a ratio > 1 of total FOXP3(+)/CD4(+) TILs in ductal carcinoma appears to represent an independent favorable prognostic factor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of FOXP3+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer depends on estrogen receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 expression status and concurrent cytotoxic T-cell infiltration.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Sep 6;16(5):432. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0432-8. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25193543 Free PMC article.
-
Metastatic triple-negative breast cancers at first relapse have fewer tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes than their matched primary breast tumors: a pilot study.Hum Pathol. 2013 Oct;44(10):2055-63. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.03.010. Epub 2013 May 21. Hum Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23701942 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse.J Clin Oncol. 2006 Dec 1;24(34):5373-80. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.05.9584. J Clin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 17135638
-
Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2020 Mar 4;20(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-6668-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32131780 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2016 Oct 18;4:59. doi: 10.1186/s40425-016-0165-6. eCollection 2016. J Immunother Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27777769 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Activation of T Cells with IL-2-Coupled Nanoparticles.Cells. 2020 Sep 9;9(9):2063. doi: 10.3390/cells9092063. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32917054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CENPF as an independent prognostic and metastasis biomarker corresponding to CD4+ memory T cells in cutaneous melanoma.Cancer Sci. 2022 Apr;113(4):1220-1234. doi: 10.1111/cas.15303. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 35189004 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting regulatory T cells for immunotherapy in melanoma.Mol Biomed. 2021;2(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s43556-021-00038-z. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Mol Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34806028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor subtypes and signature model construction based on chromatin regulators for better prediction of prognosis in uveal melanoma.Pathol Oncol Res. 2023 Jun 9;29:1610980. doi: 10.3389/pore.2023.1610980. eCollection 2023. Pathol Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 37362244 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of intra-tumoral IL17A and IL32 gene expression on T-cell responses and lymph node status in breast cancer patients.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017 Sep;143(9):1745-1756. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2431-5. Epub 2017 May 3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28470472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takagi S, Chen K, Schwarz R, Iwatsuki S, Herberman RB, Whiteside TL. Functional and phenotypic analysis of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes isolated from human primary and metastatic liver tumors and cultured in recombinant interleukin-2. Cancer. 1989;63:102–111. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890101)63:1<102::AID-CNCR2820630117>3.0.CO;2-T. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Luscher U, Filgueira L, Juretic A, Zuber M, Luscher NJ, Heberer M. et al.The pattern of cytokine gene expression in freshly excised human metastatic melanoma suggests a state of reversible anergy of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Int J Cancer. 1994;57:612–619. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570428. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

