Proteomic analysis of Terminalia chebula extract-dependent changes in human lymphoblastic T cell protein expression
- PMID: 22471968
- PMCID: PMC3382265
- DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2011.1998
Proteomic analysis of Terminalia chebula extract-dependent changes in human lymphoblastic T cell protein expression
Abstract
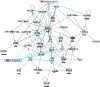
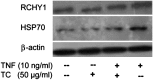
Terminalia chebula is a native plant from southern Asia to southwestern China that is used in traditional medicine for the treatment of malignant tumors and diabetes. This plant also has antibacterial and immunomodulatory properties. The present study assessed T. chebula extract-dependent protein expression changes in Jurkat cells. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry and Ingenuity Pathways Analysis (IPA) were performed to assess protein expression and networks, respectively. A comparative proteomic profile was determined in T. chebula extract (50 μg/mL)-treated and control cells; the expressions of β-tubulin, ring finger and CHY zinc finger domain containing 1, and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor kinase were significantly down-regulated in T. chebula extract-treated Jurkat cells. Moreover, the molecular basis for the T. chebula extract-dependent protein expression changes in Jurkat cells was determined by IPA. Treatment with the T. chebula extract significantly inhibited nuclear factor-κB activity and affected the proteomic profile of Jurkat cells. The molecular network signatures and functional proteomics obtained in this study may facilitate the evaluation of potential antitumor therapeutic targets and elucidate the molecular mechanism of T. chebula extract-dependent effects in Jurkat cells.
Figures
References
-
- Fabry W. Okemo PO. Ansorg R. Antibacterial activity of East African medicinal plants. J Ethnopharmacol. 1998;60:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Sabu MC. Kuttan R. Anti-diabetic activity of medicinal plants and its relationship with their antioxidant property. J Ethnopharmacol. 2002;81:155–160. - PubMed
-
- Saleem A. Husheem M. Harkonen P. Pihlaja K. Inhibition of cancer cell growth by crude extract and the phenolics of Terminalia chebula Retz. fruit. J Ethnopharmacol. 2002;81:327–336. - PubMed
-
- Reddy DB. Reddy TC. Jyotsna G, et al. Chebulagic acid, a COX-LOX dual inhibitor isolated from the fruits of Terminalia chebula Retz., induces apoptosis in COLO-205 cell line. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009;124:506–512. - PubMed
-
- Abraham RT. Weiss A. Jurkat T cells and development of the T-cell receptor signalling paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:301–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

