Lifestyle Triple P: a parenting intervention for childhood obesity
- PMID: 22471971
- PMCID: PMC3408381
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-267
Lifestyle Triple P: a parenting intervention for childhood obesity
Abstract
Background: Reversing the obesity epidemic requires the development and evaluation of childhood obesity intervention programs. Lifestyle Triple P is a parent-focused group program that addresses three topics: nutrition, physical activity, and positive parenting. Australian research has established the efficacy of Lifestyle Triple P, which aims to prevent excessive weight gain in overweight and obese children. The aim of the current randomized controlled trial is to assess the effectiveness of the Lifestyle Triple P intervention when applied to Dutch parents of overweight and obese children aged 4-8 years. This effectiveness study is called GO4fit.
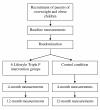
Methods/design: Parents of overweight and obese children are being randomized to either the intervention or the control group. Those assigned to the intervention condition receive the 14-week Lifestyle Triple P intervention, in which they learn a range of nutritional, physical activity and positive parenting strategies. Parents in the control group receive two brochures, web-based tailored advice, and suggestions for exercises to increase active playing at home. Measurements are taken at baseline, directly after the intervention, and at one year follow-up. Primary outcome measure is the children's body composition, operationalized as BMI z-score, waist circumference, and fat mass (biceps and triceps skinfolds). Secondary outcome measures are children's dietary behavior and physical activity level, parenting practices, parental feeding style, parenting style, parental self-efficacy, and body composition of family members (parents and siblings).
Discussion: Our intervention is characterized by a focus on changing general parenting styles, in addition to focusing on changing specific parenting practices, as obesity interventions typically do. Strengths of the current study are the randomized design, the long-term follow-up, and the broad range of both self-reported and objectively measured outcomes.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials NTR 2555 MEC AZM/UM: NL 31988.068.10 / MEC 10-3-052.
References
-
- Van Rossum CTM, Fransen HP, Verkaik-Kloosterman J, Buurma-Rethans EJM, Ocké MC. Dutch National Food Consumption Survey 2007–2010. National Institute for Public Health and the Environment, Bilthoven; 2011.
-
- Must A, Strauss RS. Risks and consequences of childhood and adolescent obesity. Int J Obes. 1999;23(Suppl 2):S2–S11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical