Effects of flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of COX and 5-lipoxygenase enzymes, on benign prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 22471974
- PMCID: PMC3448916
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01969.x
Effects of flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of COX and 5-lipoxygenase enzymes, on benign prostatic hyperplasia
Retraction in
-
Retraction statement: Effects of flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of COX and 5-lipoxygenase enzymes, on benign prostatic hyperplasia.Br J Pharmacol. 2023 Aug;180(16):2189. doi: 10.1111/bph.16153. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37269010 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and purpose: Inflammation plays a key role in the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Eicosanoids derived from the COX and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) pathways are elevated in the enlarging prostate. Flavocoxid is a novel flavonoid-based 'dual inhibitor' of the COX and 5-LOX enzymes. This study evaluated the effects of flavocoxid in experimental BPH.
Experimental approach: Rats were treated daily with testosterone propionate (3 mg·kg(-1) s.c.) or its vehicle for 14 days to induce BPH. Animals receiving testosterone were randomized to receive vehicle (1 mL·kg(-1) , i.p.) or flavocoxid (20 mg·kg(-1) , i.p.) for 14 days. Histological changes, eicosanoid content and mRNA and protein levels for apoptosis-related proteins and growth factors were assayed in prostate tissue. The effects of flavocoxid were also tested on human prostate carcinoma PC3 cells.
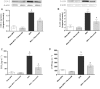
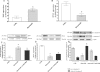
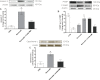
Key results: Flavocoxid reduced prostate weight and hyperplasia, blunted inducible expression of COX-2 and 5-LOX as well as the increased production of PGE(2) and leukotriene B(4) (LTB(4) ), enhanced pro-apoptotic Bax and caspase-9 and decreased the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 mRNA. Flavocoxid also reduced EGF and VEGF expression. In PC3 cells, flavocoxid stimulated apoptosis and inhibited growth factor expression. Flavocoxid-mediated induction of apoptosis was inhibited by the pan-caspase inhibitor, Z-VAD-FMK, in PC3 cells, suggesting an essential role of caspases in flavocoxid-mediated apoptosis during prostatic growth.
Conclusion and implications: Our results show that a 'dual inhibitor' of the COX and 5-LOX enzymes, such as flavocoxid, might represent a rational approach to reduce BPH through modulation of eicosanoid production and a caspase-induced apoptotic mechanism.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures




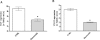
References
-
- Andrews P, Zhao X, Allen J, Li F, Chang M. A comparison of the effectiveness of selected non-steroidal anti-infl ammatory drugs and their derivatives against cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008;61:203–214. - PubMed
-
- Arruzazabala ML, Carbajal D, Mas R, Molina V, Rodríguez E, González V. Preventive effects of D-004, a lipid extract from Cuban royal palm (Roystonea regia) fruits, on prostate hyperplasia induced with testosterone in intact and castrated rodents. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 2004;30:227–233. - PubMed
-
- Barry M, Cahill RA, Roche-Nagle G, Neilan TG, Treumann A, Harmey JH, et al. Neoplasms escape selective COX-2 inhibition in an animal model of breast cancer. Ir J Med Sci. 2009;178:201–208. - PubMed
-
- Bates DO, Curry FE. Vascular endothelial growth factor increases hydraulic conductivity of isolated perfused microvessels. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:H2520–H2528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

