Redox regulation of SERCA2 is required for vascular endothelial growth factor-induced signaling and endothelial cell migration
- PMID: 22472004
- PMCID: PMC3423867
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2011.4022
Redox regulation of SERCA2 is required for vascular endothelial growth factor-induced signaling and endothelial cell migration
Abstract
Aims: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) increases angiogenesis by stimulating endothelial cell (EC) migration. VEGF-induced nitric oxide ((•)NO) release from (•)NO synthase plays a critical role, but the proteins and signaling pathways that may be redox-regulated are poorly understood. The aim of this work was to define the role of (•)NO-mediated redox regulation of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) ATPase (SERCA) in VEGF-induced signaling and EC migration.
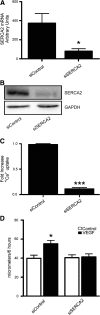
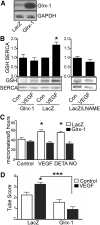
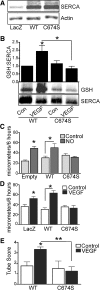
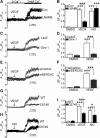
Results: VEGF-induced EC migration was prevented by the (•)NO synthase inhibitor, N (G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (LNAME). Either VEGF or (•)NO stimulated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (45)Ca(2+) uptake, a measure of SERCA activity, and knockdown of SERCA2 prevented VEGF-induced EC migration and (45)Ca(2+) uptake. S-glutathione adducts on SERCA2b, identified immunochemically, were increased by VEGF, and were prevented by LNAME or overexpression of glutaredoxin-1 (Glrx-1). Furthermore, VEGF failed to stimulate migration of ECs overexpressing Glrx-1. VEGF or (•)NO increased SERCA S-glutathiolation and stimulated migration of ECs in which wild-type (WT) SERCA2b was overexpressed with an adenovirus, but did neither in those overexpressing a C674S SERCA2b mutant, in which the reactive cysteine-674 was mutated to a serine. Increased EC Ca(2+) influx caused by VEGF or (•)NO was abrogated by overexpression of Glrx-1 or the C674S SERCA2b mutant. ER store-emptying through the ryanodine receptor (RyR) and Ca(2+) entry through Orai1 were also required for VEGF- and (•)NO-induced EC Ca(2+) influx.
Innovation and conclusions: These results demonstrate that (•)NO-mediated activation of SERCA2b via S-glutathiolation of cysteine-674 is required for VEGF-induced EC Ca(2+) influx and migration, and establish redox regulation of SERCA2b as a key component in angiogenic signaling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glutathione adducts on sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase Cys-674 regulate endothelial cell calcium stores and angiogenic function as well as promote ischemic blood flow recovery.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 18;289(29):19907-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.554451. Epub 2014 Jun 11. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24920669 Free PMC article.
-
Nox4- and Nox2-dependent oxidant production is required for VEGF-induced SERCA cysteine-674 S-glutathiolation and endothelial cell migration.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Dec 15;53(12):2327-34. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.10.546. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 23089226 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteine-674 of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase is required for the inhibition of cell migration by nitric oxide.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007 Apr;27(4):783-90. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000258413.72747.23. Epub 2007 Jan 18. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17234728
-
Targeting the redox regulation of SERCA in vascular physiology and disease.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Apr;10(2):133-8. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.11.008. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20045379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric-oxide-induced vasodilatation: regulation by physiologic s-glutathiolation and pathologic oxidation of the sarcoplasmic endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2006 May;16(4):109-14. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2006.02.001. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2006. PMID: 16713532 Review.
Cited by
-
Cysteine Glutathionylation Acts as a Redox Switch in Endothelial Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Aug 16;8(8):315. doi: 10.3390/antiox8080315. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31426416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S-glutathionylation of ion channels: insights into the regulation of channel functions, thiol modification crosstalk, and mechanosensing.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Feb 20;20(6):937-51. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5483. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 23834398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial Cell Redox Regulation of Ischemic Angiogenesis.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;67(6):458-64. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000381. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26927696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of TSP50, SERCA2 and IL-8 in Colorectal Adenoma and Carcinoma: Correlation to Clinicopathological Factors.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 Oct 21;27:1609990. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.1609990. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34744521 Free PMC article.
-
ROS signaling and redox biology in endothelial cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Sep;72(17):3281-303. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1928-9. Epub 2015 May 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25972278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adachi T. Matsui R. Weisbrod RM. Najibi S. Cohen RA. Reduced sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) uptake activity can account for the reduced response to NO, but not sodium nitroprusside, in hypercholesterolemic rabbit aorta. Circulation. 2001;104:1040–1045. - PubMed
-
- Adachi T. Schoneich C. Cohen RA. S-glutathiolation in redox-sensitive signaling. Drug Discov Today. 2005;2:39–46.
-
- Adachi T. Weisbrod RM. Pimentel DR. Ying J. Sharov VS. Schoneich C. Cohen RA. S-glutathiolation by peroxynitrite activates SERCA during arterial relaxation by nitric oxide. Nat Med. 2004;10:1200–1207. - PubMed
-
- Anger M. Samuel JL. Marotte F. Wuytack F. Rappaport L. Lompre AM. In situ mRNA distribution of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase isoforms during ontogeny in the rat. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1994;26:539–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

