Nuclear translation visualized by ribosome-bound nascent chain puromycylation
- PMID: 22472439
- PMCID: PMC3317795
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201112145
Nuclear translation visualized by ribosome-bound nascent chain puromycylation
Abstract
Whether protein translation occurs in the nucleus is contentious. To address this question, we developed the ribopuromycylation method (RPM), which visualizes translation in cells via standard immunofluorescence microscopy. The RPM is based on ribosome-catalyzed puromycylation of nascent chains immobilized on ribosomes by antibiotic chain elongation inhibitors followed by detection of puromycylated ribosome-bound nascent chains with a puromycin (PMY)-specific monoclonal antibody in fixed and permeabilized cells. The RPM correlates localized translation with myriad processes in cells and can be applied to any cell whose translation is sensitive to PMY. In this paper, we use the RPM to provide evidence for translation in the nucleoplasm and nucleolus, which is regulated by infectious and chemical stress.
Figures
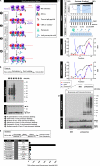
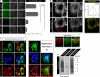
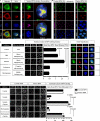
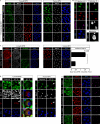

Comment in
-
The enduring enigma of nuclear translation.J Cell Biol. 2012 Apr 2;197(1):7-9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201202140. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22472436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apcher S., Daskalogianni C., Lejeune F., Manoury B., Imhoos G., Heslop L., Fåhraeus R. 2011. Major source of antigenic peptides for the MHC class I pathway is produced during the pioneer round of mRNA translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 108:11572–11577 10.1073/pnas.1104104108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

