The predictive capacity of personal genome sequencing
- PMID: 22472521
- PMCID: PMC3741669
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003380
The predictive capacity of personal genome sequencing
Abstract
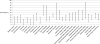
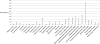
New DNA sequencing methods will soon make it possible to identify all germline variants in any individual at a reasonable cost. However, the ability of whole-genome sequencing to predict predisposition to common diseases in the general population is unknown. To estimate this predictive capacity, we use the concept of a "genometype." A specific genometype represents the genomes in the population conferring a specific level of genetic risk for a specified disease. Using this concept, we estimated the maximum capacity of whole-genome sequencing to identify individuals at clinically significant risk for 24 different diseases. Our estimates were derived from the analysis of large numbers of monozygotic twin pairs; twins of a pair share the same genometype and therefore identical genetic risk factors. Our analyses indicate that (i) for 23 of the 24 diseases, most of the individuals will receive negative test results; (ii) these negative test results will, in general, not be very informative, because the risk of developing 19 of the 24 diseases in those who test negative will still be, at minimum, 50 to 80% of that in the general population; and (iii) on the positive side, in the best-case scenario, more than 90% of tested individuals might be alerted to a clinically significant predisposition to at least one disease. These results have important implications for the valuation of genetic testing by industry, health insurance companies, public policy-makers, and consumers.
Figures

Comment in
-
What's a Genome Worth?Sci Transl Med. 2012 May 9;4(133):133fs13. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004208. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22572879
-
Comment on "the predictive capacity of personal genome sequencing".Sci Transl Med. 2012 May 23;4(135):135le3; author reply 135lr3. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004162. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22623736 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comment on "the predictive capacity of personal genome sequencing".Sci Transl Med. 2012 May 23;4(135):135le4; author reply 135lr3. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004197. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22623737 No abstract available.
-
Comment on "the predictive capacity of personal genome sequencing".Sci Transl Med. 2012 May 23;4(135):135le5; author reply 135lr3. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004126. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22623738 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bentley DR, Balasubramanian S, Swerdlow HP, Smith GP, Milton J, Brown CG, Hall KP, Evers DJ, Barnes CL, Bignell HR, Boutell JM, Bryant J, Carter RJ, Keira Cheetham R, Cox AJ, Ellis DJ, Flatbush MR, Gormley NA, Humphray SJ, Irving LJ, Karbelashvili MS, Kirk SM, Li H, Liu X, Maisinger KS, Murray LJ, Obradovic B, Ost T, Parkinson ML, Pratt MR, Rasolonjatovo IM, Reed MT, Rigatti R, Rodighiero C, Ross MT, Sabot A, Sankar SV, Scally A, Schroth GP, Smith ME, Smith VP, Spiridou A, Torrance PE, Tzonev SS, Vermaas EH, Walter K, Wu X, Zhang L, Alam MD, Anastasi C, Aniebo IC, Bailey DM, Bancarz IR, Banerjee S, Barbour SG, Baybayan PA, Benoit VA, Benson KF, Bevis C, Black PJ, Boodhun A, Brennan JS, Bridgham JA, Brown RC, Brown AA, Buermann DH, Bundu AA, Burrows JC, Carter NP, Castillo N, Chiara ECM, Chang S, Neil Cooley R, Crake NR, Dada OO, Diakoumakos KD, Dominguez-Fernandez B, Earnshaw DJ, Egbujor UC, Elmore DW, Etchin SS, Ewan MR, Fedurco M, Fraser LJ, Fuentes Fajardo KV, Scott Furey W, George D, Gietzen KJ, Goddard CP, Golda GS, Granieri PA, Green DE, Gustafson DL, Hansen NF, Harnish K, Haudenschild CD, Heyer NI, Hims MM, Ho JT, Horgan AM, Hoschler K, Hurwitz S, Ivanov DV, Johnson MQ, James T, Huw Jones TA, Kang GD, Kerelska TH, Kersey AD, Khrebtukova I, Kindwall AP, Kingsbury Z, Kokko-Gonzales PI, Kumar A, Laurent MA, Lawley CT, Lee SE, Lee X, Liao AK, Loch JA, Lok M, Luo S, Mammen RM, Martin JW, McCauley PG, McNitt P, Mehta P, Moon KW, Mullens JW, Newington T, Ning Z, Ling Ng B, Novo SM, O'Neill MJ, Osborne MA, Osnowski A, Ostadan O, Paraschos LL, Pickering L, Pike AC, Chris Pinkard D, Pliskin DP, Podhasky J, Quijano VJ, Raczy C, Rae VH, Rawlings SR, Chiva Rodriguez A, Roe PM, Rogers J, Rogert Bacigalupo MC, Romanov N, Romieu A, Roth RK, Rourke NJ, Ruediger ST, Rusman E, Sanches-Kuiper RM, Schenker MR, Seoane JM, Shaw RJ, Shiver MK, Short SW, Sizto NL, Sluis JP, Smith MA, Ernest Sohna Sohna J, Spence EJ, Stevens K, Sutton N, Szajkowski L, Tregidgo CL, Turcatti G, Vandevondele S, Verhovsky Y, Virk SM, Wakelin S, Walcott GC, Wang J, Worsley GJ, Yan J, Yau L, Zuerlein M, Mullikin JC, Hurles ME, McCooke NJ, West JS, Oaks FL, Lundberg PL, Klenerman D, Durbin R, Smith AJ. Accurate whole human genome sequencing using reversible terminator chemistry. Nature. 2008;456:53–59. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drmanac R, Sparks AB, Callow MJ, Halpern AL, Burns NL, Kermani BG, Carnevali P, Nazarenko I, Nilsen GB, Yeung G, Dahl F, Fernandez A, Staker B, Pant KP, Baccash J, Borcherding AP, Brownley A, Cedeno R, Chen L, Chernikoff D, Cheung A, Chirita R, Curson B, Ebert JC, Hacker CR, Hartlage R, Hauser B, Huang S, Jiang Y, Karpinchyk V, Koenig M, Kong C, Landers T, Le C, Liu J, McBride CE, Morenzoni M, Morey RE, Mutch K, Perazich H, Perry K, Peters BA, Peterson J, Pethiyagoda CL, Pothuraju K, Richter C, Rosenbaum AM, Roy S, Shafto J, Sharanhovich U, Shannon KW, Sheppy CG, Sun M, Thakuria JV, Tran A, Vu D, Zaranek AW, Wu X, Drmanac S, Oliphant AR, Banyai WC, Martin B, Ballinger DG, Church GM, Reid CA. Human genome sequencing using unchained base reads on self-assembling DNA nanoarrays. Science. 2010;327:78–81. - PubMed
-
- Eid J, Fehr A, Gray J, Luong K, Lyle J, Otto G, Peluso P, Rank D, Baybayan P, Bettman B, Bibillo A, Bjornson K, Chaudhuri B, Christians F, Cicero R, Clark S, Dalal R, Dewinter A, Dixon J, Foquet M, Gaertner A, Hardenbol P, Heiner C, Hester K, Holden D, Kearns G, Kong X, Kuse R, Lacroix Y, Lin S, Lundquist P, Ma C, Marks P, Maxham M, Murphy D, Park I, Pham T, Phillips M, Roy J, Sebra R, Shen G, Sorenson J, Tomaney A, Travers K, Trulson M, Vieceli J, Wegener J, Wu D, Yang A, Zaccarin D, Zhao P, Zhong F, Korlach J, Turner S. Real-time DNA sequencing from single polymerase molecules. Science. 2009;323:133–138. - PubMed
-
- Margulies M, Egholm M, Altman WE, Attiya S, Bader JS, Bemben LA, Berka J, Braverman MS, Chen YJ, Chen Z, Dewell SB, Du L, Fierro JM, Gomes XV, Godwin BC, He W, Helgesen S, Ho CH, Irzyk GP, Jando SC, Alenquer ML, Jarvie TP, Jirage KB, Kim JB, Knight JR, Lanza JR, Leamon JH, Lefkowitz SM, Lei M, Li J, Lohman KL, Lu H, Makhijani VB, McDade KE, McKenna MP, Myers EW, Nickerson E, Nobile JR, Plant R, Puc BP, Ronan MT, Roth GT, Sarkis GJ, Simons JF, Simpson JW, Srinivasan M, Tartaro KR, Tomasz A, Vogt KA, Volkmer GA, Wang SH, Wang Y, Weiner MP, Yu P, Begley RF, Rothberg JM. Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature. 2005;437:376–380. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frazer KA, Murray SS, Schork NJ, Topol EJ. Human genetic variation and its contribution to complex traits. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:241–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

