A comparison of dehydroepiandrosterone and 7-keto dehydroepiandrosterone with other drugs that modulate ethanol intake in rats responding under a multiple schedule
- PMID: 22473025
- PMCID: PMC3360959
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32835342d2
A comparison of dehydroepiandrosterone and 7-keto dehydroepiandrosterone with other drugs that modulate ethanol intake in rats responding under a multiple schedule
Abstract
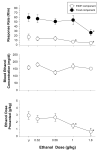
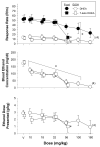
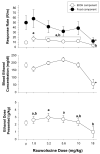
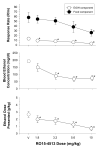
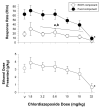
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), 7-keto DHEA, and several comparison drugs (ethanol, chlordiazepoxide, rauwolscine, and RO15-4513) were administered to male rats responding under a multiple schedule of food and ethanol presentation to determine their selectivity for decreasing ethanol-maintained responding. DHEA and 7-keto DHEA significantly decreased both ethanol-maintained and food-maintained responding, compared with the control, while also decreasing the blood ethanol concentration (BEC). Acute ethanol administration also decreased responding for both food and ethanol; however, ethanol-maintained responding was more potently decreased than food-maintained responding. BEC remained relatively stable after increasing ethanol doses. Among the other drugs tested, RO15-4513 was the most selective for decreasing ethanol-maintained responding compared with food-maintained responding, and it decreased BECs as ethanol-maintained responding decreased. The largest dose of rauwolscine significantly decreased responding for food, whereas it did not affect ethanol-maintained responding compared with the control. Low to intermediate doses of rauwolscine produced small, nonsignificant increases in ethanol-maintained responding and BECs. Chlordiazepoxide produced significant decreases in food-maintained responding and the dose of ethanol presented, but only at the highest dose tested. Although DHEA and 7-keto DHEA did not decrease ethanol-maintained responding as selectively as ethanol or RO15-4513 under the multiple schedule, these neurosteroids may be valuable pharmacological tools in the development of new treatments for alcohol abuse and dependence.
Figures
References
-
- Arsenou ES, Fousteris MA, Koutsourea AI, Nikolaropoulos SS. 7-keto-delta(5)-steroids: key-molecules owning particular biological and chemical interest. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003;3:557–567. - PubMed
-
- Balakleevsky A, Colombo G, Fadda F, Gessa GL. Ro 19-4603, a benzodiazepine receptor inverse agonist, attenuates voluntary ethanol consumption in rats selectively bred for high ethanol preference. Alcohol Alcohol. 1990;25:449–452. - PubMed
-
- Barrett JE, Weinberg ES. Effects of chlordiazepoxide on schedule-induced water and alcohol consumption in the squirrel monkey. Psychopharmacologia. 1975;40:319–328. - PubMed
-
- Belelli D, Lambert JJ. Neurosteroids: endogenous regulators of the GABA(A) receptor. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:565–575. - PubMed
-
- Belzung C, Misslin R, Vogel E, Dodd RH, Chapouthier G. Anxiogenic effects of methyl-beta-carboline-3-carboxylate in a light/dark choice situation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1987;28:29–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

