Consecutive iridium catalyzed C-C and C-H bond forming hydrogenations for the diastereo- and enantioselective synthesis of syn-3-fluoro-1-alcohols: C-H (2-fluoro)allylation of primary alcohols
- PMID: 22473044
- PMCID: PMC3448947
- DOI: 10.1039/c2cc31743e
Consecutive iridium catalyzed C-C and C-H bond forming hydrogenations for the diastereo- and enantioselective synthesis of syn-3-fluoro-1-alcohols: C-H (2-fluoro)allylation of primary alcohols
Abstract
Commercially available (2-fluoro)allyl chloride serves as an efficient allyl donor in highly enantioselective iridium catalyzed carbonyl (2-fluoro)allylations from the alcohol or aldehyde oxidation level via transfer hydrogenation. Diastereoselective Crabtree hydrogenation of the resulting homoallylic alcohols provides syn-3-fluoro-1-alcohols.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2012
Figures
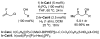



Similar articles
-
Iridium-catalyzed anti-diastereo- and enantioselective carbonyl (α-trifluoromethyl)allylation from the alcohol or aldehyde oxidation level.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2011 Apr 26;50(18):4173-5. doi: 10.1002/anie.201008296. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2011. PMID: 21472938 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Enantioselective iridium-catalyzed carbonyl allylation from the alcohol oxidation level via transfer hydrogenation: minimizing pre-activation for synthetic efficiency.Chem Commun (Camb). 2009 Dec 21;(47):7278-87. doi: 10.1039/b917243m. Epub 2009 Oct 16. Chem Commun (Camb). 2009. PMID: 20024203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enantioselective iridium-catalyzed carbonyl allylation from the alcohol or aldehyde oxidation level via transfer hydrogenative coupling of allyl acetate: departure from chirally modified allyl metal reagents in carbonyl addition.J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Nov 5;130(44):14891-9. doi: 10.1021/ja805722e. Epub 2008 Oct 8. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18841896 Free PMC article.
-
Enantioselective synthesis of alcohols and amines by iridium-catalyzed hydrogenation, transfer hydrogenation, and related processes.Chemistry. 2013 Jun 3;19(23):7274-302. doi: 10.1002/chem.201202836. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Chemistry. 2013. PMID: 23606577
-
Asymmetric Iridium-Catalyzed C-C Coupling of Chiral Diols via Site-Selective Redox-Triggered Carbonyl Addition.Top Curr Chem. 2016;372:85-101. doi: 10.1007/128_2015_651. Top Curr Chem. 2016. PMID: 26187028 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Catalytic Enantioselective C-C Coupling of Alcohols for Polyketide Total Synthesis beyond Chiral Auxiliaries and Premetalated Reagents.Chem Rev. 2024 Dec 25;124(24):13715-13735. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00858. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39642170 Review.
-
From Hydrogenation to Transfer Hydrogenation to Hydrogen Auto-Transfer in Enantioselective Metal-Catalyzed Carbonyl Reductive Coupling: Past, Present, and Future.ACS Catal. 2021 May 7;11(9):5572-5585. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.1c01109. Epub 2021 Apr 22. ACS Catal. 2021. PMID: 34306816 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging the Stereochemical Complexity of Octahedral Diastereomeric-at-Metal Catalysts to Unlock Regio-, Diastereo-, and Enantioselectivity in Alcohol-Mediated C-C Couplings via Hydrogen Transfer.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Mar 27;146(12):7905-7914. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c01857. Epub 2024 Mar 13. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38478891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catalytic Enantioselective Synthesis of Chiral Organofluorine Compounds: Alcohol-Mediated Hydrogen Transfer for Catalytic Carbonyl Reductive Coupling.Org Process Res Dev. 2019;23(5):730-736. doi: 10.1021/acs.oprd.9b00035. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Org Process Res Dev. 2019. PMID: 32982140 Free PMC article.
-
Ruthenium catalyzed reductive coupling of paraformaldehyde to trifluoromethyl allenes: CF3-bearing all-carbon quaternary centers.Org Lett. 2013 Jul 19;15(14):3790-3. doi: 10.1021/ol401771a. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Org Lett. 2013. PMID: 23841678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thayer AM. Chem Eng News. 2006;84:15.
- Mueller K, Faeh C, Diederich F. Science. 2007;317:1881. - PubMed
- Thayer AM. Chem Eng News. 2007;85:11.
-
-
For selected reviews on enantioselective methods for the preparation of organofluorine compounds, see: Ma JA, Cahard D. Chem Rev. 2004;104:6119.Brunet VA, O’Hagan D. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2008;47:1179.Bobbio C, Gouverneur V. Org Biomol Chem. 2006;4:2065.Audouard C, Ma JA, Cahard D. Adv Org Synth. 2006;2:431.Ma JA, Cahard D. Chem Rev. 2008;108:1–43.Cao LL, Gao BL, Ma ST, Liu ZP. Curr Org Chem. 2010;14:889.Kang YK, Kim DY. Curr Org Chem. 2010;14:917.Cahard D, Xu X, Couve-Bonnaire S, Pannecoucke X. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39:558.Nie J, Guo HC, Cahard D, Ma JA. Chem Rev. 2011;111:455.
-
-
-
For selected reviews on C–C bond forming hydrogenation and transfer hydrogenation, see: Patman RL, Bower JF, Kim IS, Krische MJ. Aldrichim Acta. 2008;41:95.Bower JF, Kim IS, Patman RL, Krische MJ. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2008;48:34.Han SB, Kim IS, Krische MJ. Chem Commun. 2009:7278.Bower JF, Krische MJ. Top Organomet Chem. 34:107.Hassan A, Krische MJ. Org Process Res Dev. 2011;15:1236.
-
-
-
For enantioselective carbonyl allylation via iridium catalyzed C–C bond forming transfer hydrogenation, see: Kim IS, Ngai MY, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:6340.Kim IS, Ngai MY, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:14891.Kim IS, Han SB, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:2514.Han SB, Kim IS, Han H, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:6916.Lu Y, Kim IS, Hassan A, Del Valle DJ, Krische MJ. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2009;48:5018.Han SB, Han H, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:1760.Zhang YJ, Yang JH, Kim SH, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:4562.Han SB, Gao X, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:9153.Hassan A, Zbieg JR, Krische MJ. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2011;50:3493.Gao X, Townsend IA, Krische MJ. J Org Chem. 2011;76:2350.Gao X, Zhang YJ, Krische MJ. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2011;50:4173.Hassan A, Townsend IA, Krische MJ. Chem Commun. 2011;47:10028.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

