Endothelial function in pre-pubertal children at risk of developing cardiomyopathy: a new frontier
- PMID: 22473410
- PMCID: PMC3297038
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2012(03)12
Endothelial function in pre-pubertal children at risk of developing cardiomyopathy: a new frontier
Abstract
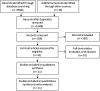
Although it is known that obesity, diabetes, and Kawasaki's disease play important roles in systemic inflammation and in the development of both endothelial dysfunction and cardiomyopathy, there is a lack of data regarding the endothelial function of pre-pubertal children suffering from cardiomyopathy. In this study, we performed a systematic review of the literature on pre-pubertal children at risk of developing cardiomyopathy to assess the endothelial function of pre-pubertal children at risk of developing cardiomyopathy. We searched the published literature indexed in PubMed, Bireme and SciELO using the keywords 'endothelial', 'children', 'pediatric' and 'infant' and then compiled a systematic review. The end points were age, the pubertal stage, sex differences, the method used for the endothelial evaluation and the endothelial values themselves. No studies on children with cardiomyopathy were found. Only 11 papers were selected for our complete analysis, where these included reports on the flow-mediated percentage dilatation, the values of which were 9.80±1.80, 5.90±1.29, 4.50±0.70, and 7.10±1.27 for healthy, obese, diabetic and pre-pubertal children with Kawasaki's disease, respectively. There was no significant difference in the dilatation, independent of the endothelium, either among the groups or between the genders for both of the measurements in children; similar results have been found in adolescents and adults. The endothelial function in cardiomyopathic children remains unclear because of the lack of data; nevertheless, the known dysfunctions in children with obesity, type 1 diabetes and Kawasaki's disease may influence the severity of the cardiovascular symptoms, the prognosis, and the mortality rate. The results of this study encourage future research into the consequences of endothelial dysfunction in pre-pubertal children.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Different corticosteroids and regimens for accelerating fetal lung maturation for babies at risk of preterm birth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 9;8(8):CD006764. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006764.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35943347 Free PMC article.
-
Transition of care for adolescents from paediatric services to adult health services.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 29;4(4):CD009794. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009794.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27128768 Free PMC article.
-
Heliox for croup in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 16;8(8):CD006822. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006822.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34397099 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Hyperlipidemia in China.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Aug 22;21:2476-84. doi: 10.12659/MSM.894246. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26297334 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular disease.Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2014 Oct 16;2014(3):291-308. doi: 10.5339/gcsp.2014.43. eCollection 2014. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2014. PMID: 25780786 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Effects of hyperlipidaemia on plasma apolipoprotein M levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an independent case-control study.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Sep 15;15(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0325-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27633510 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of periodontitis on vascular endothelial dysfunction.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 2;12:998313. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.998313. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36118034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hechter SJ, Fredriksen PM, Liu P. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in adults after the Mustard procedure. Am J Cardiol. 2001;87:660–711. - PubMed
-
- Rusconi P, Gomes-Marin O, Rossique-Gonzalvez M, Redha E, Marín J, Lon-Young M, et al. Carvedilol in children with cardiomyopathy. A 3-year experience at a single institution. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2004;23:832–8. - PubMed
-
- Azeka E, Vasconcelos LM, Cippiciani TM, Oliveira AS, Barbosa DF, Leite RMG. Insuficiência cardíaca congestiva em crianças Do tratamento farmacológico ao transplante cardíaco. Rev Med. 2008;87(2):99–104.
-
- Carvalho VO, Bocchi EA, Guimaraes GV. The Carvedilol's Beta-Blockade in Heart Failure and Exercise Training's Sympathetic Blockade in Healthy Athletes during the Rest and Peak Effort. Cardiovascular Therapeutics. 2010;28:87–92. - PubMed
-
- Guimarães GV, Bellotti G, Mocelin AO, Camargo PR, Bocchi EA. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing in children with heart failure secondary to idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Chest. 2001;120:816–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases