The omega-6 fatty acid derivative 15-deoxy-Δ¹²,¹⁴-prostaglandin J2 is involved in neuroprotection by enteric glial cells against oxidative stress
- PMID: 22473776
- PMCID: PMC3424728
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.222935
The omega-6 fatty acid derivative 15-deoxy-Δ¹²,¹⁴-prostaglandin J2 is involved in neuroprotection by enteric glial cells against oxidative stress
Abstract
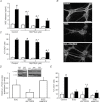
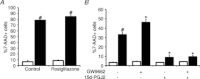
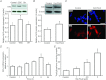
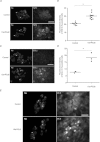
Increasing evidence suggests that enteric glial cells (EGCs) are critical for enteric neuron survival and functions. In particular, EGCs exert direct neuroprotective effects mediated in part by the release of glutathione. However, other glial factors such as those identified as regulating the intestinal epithelial barrier and in particular the omega-6 fatty acid derivative 15-deoxy-Δ¹²,¹⁴-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2) could also be involved in EGC-mediated neuroprotection. Therefore, our study aimed to assess the putative role of EGC-derived 15d-PGJ2 in their neuroprotective effects. We first showed that pretreatment of primary cultures of enteric nervous system(ENS)or humann euroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y)with 15d-PGJ2 dose dependently prevented hydrogen peroxide neurotoxicity. Furthermore, neuroprotective effects of EGCs were significantly inhibited following genetic invalidation in EGCs of the key enzyme involved in 15d-PGJ2 synthesis, i.e. L-PGDS. We next showed that 15d-PGJ2 effects were mediated by an Nrf2 dependent pathway but were not blocked by PPARγ inhibitor (GW9662) in SH-SY5Y cells and enteric neurons. Finally, 15d-PGJ2 induced a significant increase in glutamate cysteine ligase expression and intracellular glutathione in SH cells and enteric neurons. In conclusion, we identified 15d-PGJ2 as a novel glial-derived molecule with neuroprotective effects in the ENS. This study further supports the concept that omega-6 derivatives such as 15d-PGJ2 might be used in preventive and/or therapeutic strategies for the treatment of enteric neuropathies.
Figures
Comment in
-
Enteric neuroprotection.J Physiol. 2012 Jun 15;590(12):2827. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.234534. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22707588 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abdo H, Derkinderen P, Gomes P, Chevalier J, Aubert P, Masson D, Galmiche JP, Vanden Berghe P, Neunlist M, Lardeux B. Enteric glial cells protect neurons from oxidative stress in part via reduced glutathione. FASEB J. 2010;24:1082–1094. - PubMed
-
- Aoun P, Watson DG, Simpkins JW. Neuroprotective effects of PPARγ agonists against oxidative insults in HT-22 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;472:65–71. - PubMed
-
- Bush TG, Savidge TC, Freeman TC, Cox HJ, Campbell EA, Mucke L, Johnson MH, Sofroniew MV. Fulminant jejuno-ileitis following ablation of enteric glia in adult transgenic mice. Cell. 1998;93:189–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

