Prenatal immune challenge in rats: altered responses to dopaminergic and glutamatergic agents, prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle, and reduced route-based learning as a function of maternal body weight gain after prenatal exposure to poly IC
- PMID: 22473973
- PMCID: PMC3370146
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.21561
Prenatal immune challenge in rats: altered responses to dopaminergic and glutamatergic agents, prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle, and reduced route-based learning as a function of maternal body weight gain after prenatal exposure to poly IC
Abstract
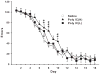
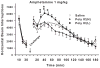
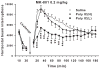
Prenatal maternal immune activation has been used to test the neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia. Most of the data are in mouse models; far less is available for rats. We previously showed that maternal weight change in response to the immune activator polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (Poly IC) in rats differentially affects offspring. Therefore, we treated gravid Harlan Sprague-Dawley rats i.p. on embryonic day 14 with 8 mg/kg of Poly IC or Saline. The Poly IC group was divided into those that lost or gained the least weight, Poly IC (L), versus those that gained the most weight, Poly IC (H), following treatment. The study design controlled for litter size, litter sampling, sex distribution, and test experience. We found no effects of Poly IC on elevated zero maze, open-field activity, object burying, light-dark test, straight channel swimming, Morris water maze spatial acquisition, reversal, or shift navigation or spatial working or reference memory, or conditioned contextual or cued fear or latent inhibition. The Poly IC (H) group showed a significant decrease in the rate of route-based learning when visible cues were unavailable in the Cincinnati water maze and reduced prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in females, but not males. The Poly IC (L) group exhibited altered responses to acute pharmacological challenges: exaggerated hyperactivity in response to (+)-amphetamine and an attenuated hyperactivity in response to MK-801. This model did not exhibit the cognitive, or latent inhibition deficits reported in Poly IC-treated rats but showed changes in response to drugs acting on neurotransmitter systems implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia (dopaminergic hyperfunction and glutamatergic hypofunction).
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Neil M. Richtand discloses the following relationships: Consultant to Bristol-Meyers Squibb, Gerson Lehrman Group, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc./Sepracor. Speaker’s Bureau: Bristol-Meyers Squibb, Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Schering-Plough Corporation/Merck, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc./Sepracor, and Grant/Research Support: Ortho-McNeil Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC; AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prenatal immune challenge in rats: effects of polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid on spatial learning, prepulse inhibition, conditioned fear, and responses to MK-801 and amphetamine.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2015 Jan-Feb;47:54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2014.10.007. Epub 2014 Nov 8. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2015. PMID: 25450663 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of perinatal exposure to antidepressants on learning and memory, acoustic startle, anxiety, and open-field activity in Sprague-Dawley rats.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2017 Oct;61:92-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2017.06.004. Epub 2017 Jun 24. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28655626
-
Deficient prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in Hooded-Wistar rats compared with Sprague-Dawley rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2003 Apr;30(4):254-61. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2003.03823.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12680843
-
Perinatal exposure to the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram alters spatial learning and memory, anxiety, depression, and startle in Sprague-Dawley rats.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2016 Nov;54:39-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2016.08.007. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27591973
-
Distinct periods of developmental sensitivity to the effects of 3,4-(±)-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on behaviour and monoamines in rats.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012 Jul;15(6):811-24. doi: 10.1017/S1461145711000952. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21733225 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evidence for a dysregulated immune system in the etiology of psychiatric disorders.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;8(4):900-20. doi: 10.1007/s11481-013-9462-8. Epub 2013 May 5. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23645137 Review.
-
Disruption of social approach by MK-801, amphetamine, and fluoxetine in adolescent C57BL/6J mice.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2013 Mar-Apr;36:36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2012.07.007. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2013. PMID: 22898204 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(I:C)-induced maternal immune activation causes elevated self-grooming in male rat offspring: Involvement of abnormal postpartum static nursing in dam.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 16;11:1054381. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1054381. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37009477 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Immune Activation during Early or Late Gestation on N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Measures in Adult Rat Offspring.Front Psychiatry. 2017 Sep 4;8:77. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00077. eCollection 2017. Front Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28928676 Free PMC article.
-
Heightened fear in response to a safety cue and extinguished fear cue in a rat model of maternal immune activation.Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 May 7;8:168. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00168. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24847231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashdown H, Dumont Y, Ng M, Poole S, Boksa P, Luheshi GN. The role of cytokines in mediating effects of prenatal infection on the fetus: implications for schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2006;11:47–55. - PubMed
-
- Bailey KR, Rustay NR, Crawley JN. Behavioral phenotyping of transgenic and knockout mice: practical concerns and potential pitfalls. ILAR J. 2006;47:124–131. - PubMed
-
- Bitanihirwe BK, Weber L, Feldon J, Meyer U. Cognitive impairment following prenatal immune challenge in mice correlates with prefrontal cortical AKT1 deficiency. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010b;13:981–996. - PubMed
-
- Boksa P. Effects of prenatal infection on brain development and behavior: a review of findings from animal models. Brain Behav Immun. 2010;24:881–897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
