Deep intron elements mediate nested splicing events at consecutive AG dinucleotides to regulate alternative 3' splice site choice in vertebrate 4.1 genes
- PMID: 22473990
- PMCID: PMC3372232
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.05716-11
Deep intron elements mediate nested splicing events at consecutive AG dinucleotides to regulate alternative 3' splice site choice in vertebrate 4.1 genes
Abstract
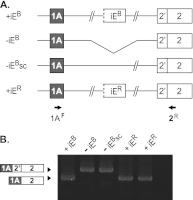
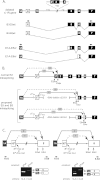
Distal intraexon (iE) regulatory elements in 4.1R pre-mRNA govern 3' splice site choice at exon 2 (E2) via nested splicing events, ultimately modulating expression of N-terminal isoforms of cytoskeletal 4.1R protein. Here we explored intrasplicing in other normal and disease gene contexts and found conservation of intrasplicing through vertebrate evolution. In the paralogous 4.1B gene, we identified ∼120 kb upstream of E2 an ultradistal intraexon, iE(B), that mediates intrasplicing by promoting two intricately coupled splicing events that ensure selection of a weak distal acceptor at E2 (E2dis) by prior excision of the competing proximal acceptor (E2prox). Mutating iE(B) in minigene splicing reporters abrogated intrasplicing, as did blocking endogenous iE(B) function with antisense morpholinos in live mouse and zebrafish animal models. In a human elliptocytosis patient with a mutant 4.1R gene lacking E2 through E4, we showed that aberrant splicing is consistent with iE(R)-mediated intrasplicing at the first available exons downstream of iE(R), namely, alternative E5 and constitutive E6. Finally, analysis of heterologous acceptor contexts revealed a strong preference for nested 3' splice events at consecutive pairs of AG dinucleotides. Distal regulatory elements may control intrasplicing at a subset of alternative 3' splice sites in vertebrate pre-mRNAs to generate proteins with functional diversity.
Figures




References
-
- Auboeuf D, Batsche E, Dutertre M, Muchardt C, O'Malley BW. 2007. Coregulators: transducing signal from transcription to alternative splicing. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 18:122–129 - PubMed
-
- Baklouti F, et al. 1997. Organization of the human protein 4.1 genomic locus: new insights into the tissue-specific alternative splicing of the pre-mRNA. Genomics 39:289–302 - PubMed
-
- Baklouti F, et al. 2011. Homozygous deletion of EPB41 genuine AUG-containing exons results in mRNA splicing defects, NMD activation and protein 4.1R complete deficiency in hereditary elliptocytosis. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 47:158–165 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
