The Asp299Gly polymorphism alters TLR4 signaling by interfering with recruitment of MyD88 and TRIF
- PMID: 22474023
- PMCID: PMC3531971
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200202
The Asp299Gly polymorphism alters TLR4 signaling by interfering with recruitment of MyD88 and TRIF
Abstract
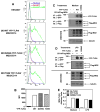
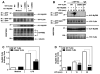
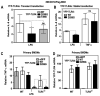
Asp(299)Gly (D299G) and, to a lesser extent, Thr(399)Ile (T399I) TLR4 polymorphisms have been associated with gram-negative sepsis and other infectious diseases, but the mechanisms by which they affect TLR4 signaling are unclear. In this study, we determined the impact of the D299G and T399I polymorphisms on TLR4 expression, interactions with myeloid differentiation factor 2 (MD2), LPS binding, and LPS-mediated activation of the MyD88- and Toll/IL-1R resistance domain-containing adapter inducing IFN-β (TRIF) signaling pathways. Complementation of human embryonic kidney 293/CD14/MD2 transfectants with wild-type (WT) or mutant yellow fluorescent protein-tagged TLR4 variants revealed comparable total TLR4 expression, TLR4-MD2 interactions, and LPS binding. FACS analyses with anti-TLR4 Ab showed only minimal changes in the cell-surface levels of the D299G TLR4. Cells transfected with D299G TLR4 exhibited impaired LPS-induced phosphorylation of p38 and TANK-binding kinase 1, activation of NF-κB and IFN regulatory factor 3, and induction of IL-8 and IFN-β mRNA, whereas T399I TLR4 did not cause statistically significant inhibition. In contrast to WT TLR4, expression of the D299G mutants in TLR4(-/-) mouse macrophages failed to elicit LPS-mediated induction of TNF-α and IFN-β mRNA. Coimmunoprecipitation revealed diminished LPS-driven interaction of MyD88 and TRIF with the D299G TLR4 species, in contrast to robust adapter recruitment exhibited by WT TLR4. Thus, the D299G polymorphism compromises recruitment of MyD88 and TRIF to TLR4 without affecting TLR4 expression, TLR4-MD2 interaction, or LPS binding, suggesting that it interferes with TLR4 dimerization and assembly of intracellular docking platforms for adapter recruitment.
Figures
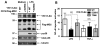


Similar articles
-
Endotoxin tolerance dysregulates MyD88- and Toll/IL-1R domain-containing adapter inducing IFN-beta-dependent pathways and increases expression of negative regulators of TLR signaling.J Leukoc Biol. 2009 Oct;86(4):863-75. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0309189. Epub 2009 Aug 5. J Leukoc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19656901 Free PMC article.
-
CD14 dependence of TLR4 endocytosis and TRIF signaling displays ligand specificity and is dissociable in endotoxin tolerance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 7;112(27):8391-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424980112. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26106158 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin modulates TLR4-mediated inflammatory genes through MyD88- and TRIF-dependent signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.J Pineal Res. 2012 Nov;53(4):325-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.01002.x. Epub 2012 Apr 27. J Pineal Res. 2012. PMID: 22537289
-
TRIF signaling is essential for TLR4-driven IgE class switching.J Immunol. 2014 Mar 15;192(6):2651-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300909. Epub 2014 Feb 14. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24532577 Free PMC article.
-
Human TLR4 polymorphism D299G/T399I alters TLR4/MD-2 conformation and response to a weak ligand monophosphoryl lipid A.Int Immunol. 2013 Jan;25(1):45-52. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxs084. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Int Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22962435
Cited by
-
Toll-Like Receptor Signaling in Depression.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020 Nov;121:104843. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2020.104843. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020. PMID: 32911436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptor 4 D299G polymorphism in metabolic disorders: a meta-analysis.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Apr;40(4):3015-20. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2374-5. Epub 2012 Dec 29. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23275193
-
Structural analyses of human Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms D299G and T399I.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 23;287(48):40611-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.404608. Epub 2012 Oct 10. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23055527 Free PMC article.
-
The R753Q polymorphism in Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) attenuates innate immune responses to mycobacteria and impairs MyD88 adapter recruitment to TLR2.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 23;292(25):10685-10695. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.784470. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28442574 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling Interindividual Variability of Human Fibroblast Innate Immune Response Using Robust Cell-Based Protocols.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 11;11:569331. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.569331. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33505391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA., Jr A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature. 1997;388:394–397. - PubMed
-
- Schattgen SA, Fitzgerald KA. The PYHIN protein family as mediators of host defenses. Immunol Rev. 2011;243:109–118. - PubMed
-
- Onoguchi K, Yoneyama M, Fujita T. Retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptors. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011;31:27–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

