Skeletal muscle protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B regulates insulin sensitivity in African Americans
- PMID: 22474028
- PMCID: PMC3357297
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-0744
Skeletal muscle protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B regulates insulin sensitivity in African Americans
Abstract
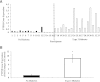
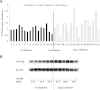
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) is postulated to modulate insulin action by dephosphorylating the insulin receptor signaling proteins and attenuating insulin signaling. We sought to determine the relationship of skeletal muscle PTP1B to whole-body insulin sensitivity. We studied 17 African Americans with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and 16 without diabetes. PTP1B gene expression and protein abundance were determined in the biopsied skeletal muscles at the baseline of a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. PTP1B gene expression was significantly higher in subjects with T2DM versus control (P < 0.0001) and remained significantly different after adjusting for age and insulin sensitivity (P = 0.05). PTP1B gene expression was positively related to protein abundance (r(s) = 0.39; P = 0.03; adjusted for age and insulin sensitivity) and negatively related to insulin sensitivity (r(s) = -0.52; P = 0.002; adjusted for age). Overexpression and interference RNA of PTP1B were performed in primary human skeletal muscle culture. PTP1B overexpression resulted in reduction of Akt phosphorylation in the control subjects. Moreover, interference RNA transfection downregulated PTP1B expression and enhanced Akt phosphorylation in subjects with T2DM. These data show that skeletal muscle PTP1B gene expression is increased in African American subjects with T2DM, is negatively associated with whole-body insulin sensitivity, and contributes to modulation of insulin signaling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chronic ethanol consumption up-regulates protein-tyrosine phosphatase-1B (PTP1B) expression in rat skeletal muscle.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Dec;31(12):1576-82. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.161. Epub 2010 Nov 22. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010. PMID: 21102485 Free PMC article.
-
Early growth response-1 negative feedback regulates skeletal muscle postprandial insulin sensitivity via activating Ptp1b transcription.FASEB J. 2018 Aug;32(8):4370-4379. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701340R. Epub 2018 Mar 15. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29543533
-
Modulation of cellular insulin signaling and PTP1B effects by lipid metabolites in skeletal muscle cells.J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Aug;24(8):1529-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.12.014. Epub 2013 Mar 6. J Nutr Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23481236 Free PMC article.
-
The role of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications.J Physiol Biochem. 2022 May;78(2):307-322. doi: 10.1007/s13105-021-00860-7. Epub 2022 Jan 6. J Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34988903 Review.
-
PTP1B and TCPTP--nonredundant phosphatases in insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis.FEBS J. 2013 Jan;280(2):445-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08563.x. Epub 2012 Apr 18. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 22404968 Review.
Cited by
-
Promising Inhibitory Effects of Anthraquinones, Naphthopyrone, and Naphthalene Glycosides, from Cassia obtusifolia on α-Glucosidase and Human Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases 1B.Molecules. 2016 Dec 27;22(1):28. doi: 10.3390/molecules22010028. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 28035984 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular RNAs Are Associated With Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Phenotypes.Diabetes Care. 2017 Apr;40(4):546-553. doi: 10.2337/dc16-1354. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Diabetes Care. 2017. PMID: 28183786 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting density-enhanced phosphatase-1 (DEP-1) with antisense oligonucleotides improves the metabolic phenotype in high-fat diet-fed mice.Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Jul 26;11:49. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-11-49. Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 23889985 Free PMC article.
-
Protamine zinc insulin combined with sodium selenite improves glycometabolism in the diabetic KKAy mice.Sci Rep. 2016 May 23;6:26563. doi: 10.1038/srep26563. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27212152 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring New Drug Targets for Type 2 Diabetes: Success, Challenges and Opportunities.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 31;10(2):331. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020331. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203540 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeFronzo RA. Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and coronary artery disease: a complex metabolic web. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1992;20(Suppl. 11):S1–S16 - PubMed
-
- Haffner SM. The insulin resistance syndrome revisited. Diabetes Care 1996;19:275–277 - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988;37:1595–1607 - PubMed
-
- White MF, Kahn CR. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem 1994;269:1–4 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

