Changes in treatment adherence and glycemic control during the transition to adolescence in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 22474040
- PMCID: PMC3357213
- DOI: 10.2337/dc11-2163
Changes in treatment adherence and glycemic control during the transition to adolescence in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To test models of unidirectional and bidirectional change between treatment adherence and glycemic control in youth with type 1 diabetes.
Research design and methods: We conducted a 2-year longitudinal, multisite study of 225 youth with type 1 diabetes recruited at the cusp of adolescence (aged 9-11 years) to describe the mutual influences of glycemic control as measured by HbA(1c) and treatment adherence as measured by blood glucose monitoring frequency (BGMF) during the transition to adolescence.
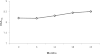
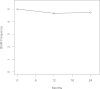
Results: HbA(1c) increased from 8.2 to 8.6% (P < 0.001) and BGMF decreased from 4.9 to 4.5 checks per day (P < 0.02) during the 2-year period. Changes in the BGMF slope predicted changes in HbA(1c). A change (increase) in HbA(1c) was associated with a change (decrease) in BGMF of 1.26 (P < 0.001) after controlling for covariates.
Conclusions: The magnitude of the effect of declining treatment adherence (BGMF) on glycemic control in young adolescents may be even greater than declines observed among older adolescents. BGMF offers a powerful tool for targeted management of glycemic control for type 1 diabetes during the critical transition to adolescence.
Figures
References
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group Effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the development and progression of long-term complications in adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. J Pediatr 1994;125:177–188 - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM, Zinman B, Cleary PA, et al. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Research Group Modern-day clinical course of type 1 diabetes mellitus after 30 years’ duration: the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications and Pittsburgh epidemiology of diabetes complications experience (1983-2005). Arch Intern Med 2009;169:1307–1316 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kovacs M, Goldston D, Obrosky DS, Iyengar S. Prevalence and predictors of pervasive noncompliance with medical treatment among youths with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1992;31:1112–1119 - PubMed
-
- Hood KK, Peterson CM, Rohan JM, Drotar D. Association between adherence and glycemic control in pediatric type 1 diabetes: a meta-analyses. Pediatrics 2009;124:e1171–e1179 - PubMed
-
- Jacobson AM, Hauser ST, Lavori P, et al. Family environment and glycemic control: a four-year prospective study of children and adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Psychosom Med 1994;56:401–409 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous