Seipin: from human disease to molecular mechanism
- PMID: 22474068
- PMCID: PMC3351812
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R023754
Seipin: from human disease to molecular mechanism
Abstract
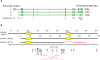
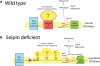
The most-severe form of congenital generalized lipodystrophy (CGL) is caused by mutations in BSCL2/seipin. Seipin is a homo-oligomeric integral membrane protein in the endoplasmic reticulum that concentrates at junctions with cytoplasmic lipid droplets (LDs). While null mutations in seipin are responsible for lipodystrophy, dominant mutations cause peripheral neuropathy and other nervous system pathologies. We first review the clinical aspects of CGL and the discovery of the responsible genetic loci. The structure of seipin, its normal isoforms, and mutations found in patients are then presented. While the function of seipin is not clear, seipin gene manipulation in yeast, flies, mice, and human cells has recently yielded a trove of information that suggests roles in lipid metabolism and LD assembly and maintenance. A model is presented that attempts to bridge these new data to understand the role of this fascinating protein.
Figures
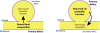
References
-
- Mitchell S. W. 1885. Singular case of absence of adipose matter in the upper half of the body. Am. J. Med. Sci. 179: 105–106
-
- Lawrence R. D. 1946. Lipodystrophy and hepatomegaly, with diabetes, lipaemia, and other metabolic disturbances: a case throwing new light on the action of insulin. Lancet. 1: 724–731, 773–775 - PubMed
-
- Berardinelli W. 1954. An undiagnosed endocrinometabolic syndrome: report of 2 cases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 14: 193–204 - PubMed
-
- Seip M. 1959. Lipodystrophy and gigantism with associated endocrine manifestations. A new diencephalic syndrome? Acta Paediatr. 48: 555–574 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

