Hydrogen sulfide induced disruption of Na+ homeostasis in the cortex
- PMID: 22474073
- PMCID: PMC3391029
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfs125
Hydrogen sulfide induced disruption of Na+ homeostasis in the cortex
Abstract
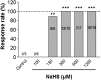
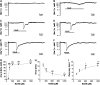
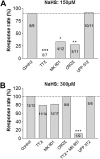
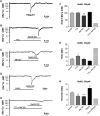
Maintenance of ionic balance is essential for neuronal functioning. Hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S), a known toxic environmental gaseous pollutant, has been recently recognized as a gasotransmitter involved in numerous biological processes and is believed to play an important role in the neural activities under both physiological and pathological conditions. However, it is unclear if it plays any role in maintenance of ionic homeostasis in the brain under physiological/pathophysiological conditions. Here, we report by directly measuring Na(+) activity using Na(+) selective electrodes in mouse cortical slices that H(2)S donor sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) increased Na(+) influx in a concentration-dependent manner. This effect could be partially blocked by either Na(+) channel blocker or N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) blocker alone or almost completely abolished by coapplication of both blockers but not by non-NMDAR blocker. These data suggest that increased H(2)S in pathophysiological conditions, e.g., hypoxia/ischemia, potentially causes a disruption of ionic homeostasis by massive Na(+) influx through Na(+) channels and NMDARs, thus injuring neural functions. Activation of delta-opioid receptors (DOR), which reduces Na(+) currents/influx in normoxia, had no effect on H(2)S-induced Na(+) influx, suggesting that H(2)S-induced disruption of Na(+) homeostasis is resistant to DOR regulation and may play a major role in neuronal injury in pathophysiological conditions, e.g., hypoxia/ischemia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DOR activation inhibits anoxic/ischemic Na+ influx through Na+ channels via PKC mechanisms in the cortex.Exp Neurol. 2012 Aug;236(2):228-39. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 May 15. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22609332 Free PMC article.
-
delta-Opioid receptors protect from anoxic disruption of Na+ homeostasis via Na+ channel regulation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Nov;66(21):3505-16. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0136-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19756387 Free PMC article.
-
delta-, but not mu-, opioid receptor stabilizes K(+) homeostasis by reducing Ca(2+) influx in the cortex during acute hypoxia.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Jul;212(1):60-7. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21000. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17373650
-
[Cerebral ischemia-hypoxia and biophysical mechanisms of neurodegeneration and neuroprotection effects].Fiziol Zh (1994). 2003;49(2):7-12. Fiziol Zh (1994). 2003. PMID: 12945108 Review. Ukrainian.
-
Ionic storm in hypoxic/ischemic stress: can opioid receptors subside it?Prog Neurobiol. 2010 Apr;90(4):439-70. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.12.007. Epub 2009 Dec 28. Prog Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20036308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DOR activation inhibits anoxic/ischemic Na+ influx through Na+ channels via PKC mechanisms in the cortex.Exp Neurol. 2012 Aug;236(2):228-39. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 May 15. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22609332 Free PMC article.
-
The Ying and Yang of Hydrogen Sulfide as a Paracrine/Autocrine Agent in Neurodegeneration: Focus on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Cells. 2023 Jun 22;12(13):1691. doi: 10.3390/cells12131691. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aggravation of seizure-like events by hydrogen sulfide: involvement of multiple targets that control neuronal excitability.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014 May;20(5):411-9. doi: 10.1111/cns.12228. Epub 2014 Jan 31. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014. PMID: 24479764 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional events co-regulated by hypoxia and cold stresses in Zebrafish larvae.BMC Genomics. 2015 May 15;16(1):385. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1560-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25975375 Free PMC article.
-
Ambient geothermal hydrogen sulfide exposure and peripheral neuropathy.Neurotoxicology. 2017 May;60:10-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2017.02.006. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Neurotoxicology. 2017. PMID: 28223159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarts M, Liu Y, Liu L, Besshoh S, Arundine M, Gurd JW, Wang Y-T, Salter MW. Treatment of ischemic brain damage by perturbing NMDA receptor-PSD-95 protein interactions. Science. 2002;298:846–850. - PubMed
-
- Aizenman E, Lipton SA, Loring RH. Selective modulation of NMDA responses by reduction and oxidation. Neuron. 1989;2:1257–1263. - PubMed
-
- Balboni G, Salvadori S, Guerrini R, Negri L, Giannini E, Jinsmaa Y, Bryant SD, Lazarus LH. Potent δ-opioid receptor agonists containing the Dmt-Tic pharmacophore. J. Med. Chem. 2002;45:5556–5563. - PubMed
-
- Banasiak KJ, Burenkova O, Haddad GG. Activation of voltage-sensitive sodium channels during oxygen deprivation leads to apoptotic neuronal death. Neuroscience. 2004;126:31–44. - PubMed

