Whole exome sequencing to identify a novel gene (caveolin-1) associated with human pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 22474227
- PMCID: PMC3380156
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.111.961888
Whole exome sequencing to identify a novel gene (caveolin-1) associated with human pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Background: Heritable and idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) are phenotypically identical and associated with mutations in several genes related to transforming growth factor (TGF) beta signaling, including bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2, activin receptor-like kinase 1, endoglin, and mothers against decapentaplegic 9. Approximately 25% of heritable cases lack identifiable mutations in any of these genes.
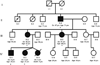
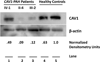
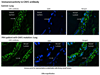
Methods and results: We used whole exome sequencing to study a 3-generation family with multiple affected family members with PAH, but no identifiable TGF beta mutation. We identified a frameshift mutation in caveolin-1 (CAV1), which encodes a membrane protein of caveolae abundant in the endothelium and other cells of the lung. An independent de novo frameshift mutation was identified in a child with idiopathic PAH. Western blot analysis demonstrated a reduction in caveolin-1 protein, while lung tissue immunostaining studies demonstrated a reduction in normal caveolin-1 density within the endothelial cell layer of small arteries.
Conclusions: Our study represents successful elucidation of a dominant Mendelian disorder using whole exome sequencing. Mutations in CAV1 are associated in rare cases with PAH. This may have important implications for pulmonary vascular biology, as well as PAH-directed therapeutic development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
Novel inheritable caveolin-1 mutations in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2012 Dec;5(6):706-7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.112.965335. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2012. PMID: 23250901 No abstract available.
References
-
- Humbert M, Sitbon O, Chaouat A, Bertocchi M, Habib G, Gressin V, et al. Survival in patients with idiopathic, familial, and anorexigen-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the modern management era. Circulation. 2010;122:156–163. - PubMed
-
- Simonneau G, Robbins IM, Beghetti M, Channick RN, Delcroix M, Denton CP, et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:S43–S54. - PubMed
-
- Badesch DB, Raskob GE, Elliott CG, Krichman AM, Farber HW, Frost AE, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: baseline characteristics from the REVEAL Registry. Chest. 2010;137:376–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK58404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 RR024978/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- EY08126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY008126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060056/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HD15052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL072058/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD015052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024977/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK59637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL098743/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

