Casein kinase 2-mediated synaptic GluN2A up-regulation increases N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activity and excitability of hypothalamic neurons in hypertension
- PMID: 22474321
- PMCID: PMC3366779
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.331165
Casein kinase 2-mediated synaptic GluN2A up-regulation increases N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activity and excitability of hypothalamic neurons in hypertension
Abstract
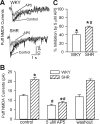
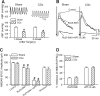
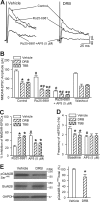
Increased glutamatergic input, particularly N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) activity, in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus is closely associated with high sympathetic outflow in essential hypertension. The molecular mechanisms underlying augmented NMDAR activity in hypertension are unclear. GluN2 subunit composition at the synaptic site critically determines NMDAR functional properties. Here, we found that evoked NMDAR-excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) of retrogradely labeled spinally projecting PVN neurons displayed a larger amplitude and shorter decay time in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) than in Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats. Blocking GluN2B caused a smaller decrease in NMDAR-EPSCs of PVN neurons in SHRs than in WKY rats. In contrast, GluN2A blockade resulted in a larger reduction in evoked NMDAR-EPSCs and puff NMDA-elicited currents of PVN neurons in SHRs than in WKY rats. Blocking presynaptic GluN2A, but not GluN2B, significantly reduced the frequency of miniature EPSCs and the firing activity of PVN neurons in SHRs. The mRNA and total protein levels of GluN2A and GluN2B in the PVN were greater in SHRs than in WKY rats. Furthermore, the GluN2B Ser(1480) phosphorylation level and the synaptosomal GluN2A protein level in the PVN were significantly higher in SHRs than in WKY rats. Inhibition of protein kinase CK2 normalized the GluN2B Ser(1480) phosphorylation level and the contribution of GluN2A to NMDAR-EPSCs and miniature EPSCs of PVN neurons in SHRs. Collectively, our findings suggest that CK2-mediated GluN2B phosphorylation contributes to increased synaptic GluN2A, which potentiates pre- and postsynaptic NMDAR activity and the excitability of PVN presympathetic neurons in hypertension.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Endogenous casein kinase-1 modulates NMDA receptor activity of hypothalamic presympathetic neurons and sympathetic outflow in hypertension.J Physiol. 2015 Oct 1;593(19):4439-52. doi: 10.1113/JP270831. Epub 2015 Aug 18. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26174743 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKII Regulates Synaptic NMDA Receptor Activity of Hypothalamic Presympathetic Neurons and Sympathetic Outflow in Hypertension.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 1;37(44):10690-10699. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2141-17.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 2. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28972129 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of sympathetic vasomotor activity by the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in normotensive and hypertensive states.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):H1200-H1214. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00216.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30095973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase CK2 increases glutamatergic input in the hypothalamus and sympathetic vasomotor tone in hypertension.J Neurosci. 2011 Jun 1;31(22):8271-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1147-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21632948 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamatergic Regulation of Hypothalamic Presympathetic Neurons in Hypertension.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017 Sep 19;19(10):78. doi: 10.1007/s11906-017-0776-4. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017. PMID: 28929331 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired Hypothalamic Regulation of Sympathetic Outflow in Primary Hypertension.Neurosci Bull. 2019 Feb;35(1):124-132. doi: 10.1007/s12264-018-0316-5. Epub 2018 Dec 1. Neurosci Bull. 2019. PMID: 30506315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous casein kinase-1 modulates NMDA receptor activity of hypothalamic presympathetic neurons and sympathetic outflow in hypertension.J Physiol. 2015 Oct 1;593(19):4439-52. doi: 10.1113/JP270831. Epub 2015 Aug 18. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26174743 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKII Regulates Synaptic NMDA Receptor Activity of Hypothalamic Presympathetic Neurons and Sympathetic Outflow in Hypertension.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 1;37(44):10690-10699. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2141-17.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 2. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28972129 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of sympathetic vasomotor activity by the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in normotensive and hypertensive states.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):H1200-H1214. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00216.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30095973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NMDA Receptor Plasticity in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Contributes to the Elevated Blood Pressure Produced by Angiotensin II.J Neurosci. 2015 Jul 1;35(26):9558-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2301-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26134639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carretero O. A., Oparil S. (2000) Essential hypertension: part I, definition and etiology. Circulation 101, 329–335 - PubMed
-
- Oparil S., Zaman M. A., Calhoun D. A. (2003) Pathogenesis of hypertension. Ann. Intern. Med. 139, 761–776 - PubMed
-
- Judy W. V., Watanabe A. M., Henry D. P., Besch H. R., Jr., Murphy W. R., Hockel G. M. (1976) Sympathetic nerve activity: role in regulation of blood pressure in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Circ. Res. 38, 21–29 - PubMed
-
- Anderson E. A., Sinkey C. A., Lawton W. J., Mark A. L. (1989) Elevated sympathetic nerve activity in borderline hypertensive humans: evidence from direct intraneural recordings. Hypertension 14, 177–183 - PubMed
-
- Li D. P., Pan H. L. (2007) Glutamatergic inputs in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus maintain sympathetic vasomotor tone in hypertension. Hypertension 49, 916–925 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

