Properties of the human Cdc45/Mcm2-7/GINS helicase complex and its action with DNA polymerase epsilon in rolling circle DNA synthesis
- PMID: 22474384
- PMCID: PMC3341058
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1203734109
Properties of the human Cdc45/Mcm2-7/GINS helicase complex and its action with DNA polymerase epsilon in rolling circle DNA synthesis
Abstract
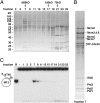
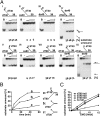
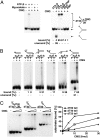
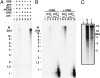
In eukaryotes, although the Mcm2-7 complex is a key component of the replicative DNA helicase, its association with Cdc45 and GINS (the CMG complex) is required for the activation of the DNA helicase. Here, we show that the CMG complex is localized to chromatin in human cells and describe the biochemical properties of the human CMG complex purified from baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells. The isolated complex binds to ssDNA regions in the presence of magnesium and ATP (or a nonhydrolyzable ATP analog), contains maximal DNA helicase in the presence of forked DNA structures, and translocates along the leading strand (3' to 5' direction). The complex hydrolyses ATP in the absence of DNA; unwinds duplex regions up to 500 bp; and either replication protein A or Escherichia coli single stranded binding protein increases the efficiency of displacement of long duplex regions. Using a 200-nt primed circular DNA substrate, the combined action of human DNA polymerase ε and the human CMG complex leads to the formation of products >10 kb in length. These findings suggest that the coordinated action of these replication complexes supports leading strand synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tanaka S, Araki H. Regulation of the initiation step of DNA replication by cyclin-dependent kinases. Chromosoma. 2010;119:565–574. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka S, et al. CDK-dependent phosphorylation of Sld2 and Sld3 initiates DNA replication in budding yeast. Nature. 2007;445:328–332. - PubMed
-
- Zegerman P, Diffley JF. Phosphorylation of Sld2 and Sld3 by cyclin-dependent kinases promotes DNA replication in budding yeast. Nature. 2007;445:281–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

