Preventing bacterial DNA release and absent in melanoma 2 inflammasome activation by a Legionella effector functioning in membrane trafficking
- PMID: 22474394
- PMCID: PMC3341053
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1117490109
Preventing bacterial DNA release and absent in melanoma 2 inflammasome activation by a Legionella effector functioning in membrane trafficking
Abstract
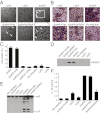
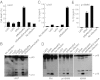
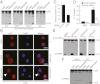
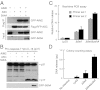
Legionella pneumophila, the causative agent of Legionnaires' pneumonia, resides in a distinct vacuole structure called Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV). The LCV resists fusion with the lysosome and permits efficient bacterial replication in host macrophages, which requires a Dot/Icm type IVB secretion system. Dot/Icm-translocated effector SdhA is critical for L. pneumophila intracellular growth and functions to prevent host cell death. Here, we show that the absence of SdhA resulted in elevated caspase-1 activation and IL-1β secretion as well as macrophage pyroptosis during Legionella infection. These inflammasome activation phenotypes were independent of the established flagellin-NAIP5-NLRC4 axis, but relied on the DNA-sensing AIM2 inflammasome. We further demonstrate that Legionella DNA was released into macrophage cytosol, and this effect was significantly exaggerated by the absence of SdhA. SdhA bears a functional Golgi-targeting GRIP domain that is required for preventing AIM2 inflammasome activation. Ectopically expressed SdhA formed a unique ring-shape membrane structure, further indicating a role in membrane trafficking and maintaining LCV membrane integrity. Our data together suggest a possible link, mediated by the function of SdhA, between LCV trafficking/maturation and suppression of host innate immune detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Berger KH, Isberg RR. Two distinct defects in intracellular growth complemented by a single genetic locus in Legionella pneumophila. Mol Microbiol. 1993;7:7–19. - PubMed
-
- Vogel JP, Andrews HL, Wong SK, Isberg RR. Conjugative transfer by the virulence system of Legionella pneumophila. Science. 1998;279:873–876. - PubMed
-
- Hubber A, Roy CR. Modulation of host cell function by Legionella pneumophila type IV effectors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010;26:261–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

