TXNIP links innate host defense mechanisms to oxidative stress and inflammation in retinal Muller glia under chronic hyperglycemia: implications for diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 22474421
- PMCID: PMC3313582
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/438238
TXNIP links innate host defense mechanisms to oxidative stress and inflammation in retinal Muller glia under chronic hyperglycemia: implications for diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
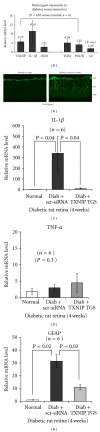
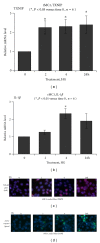
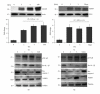
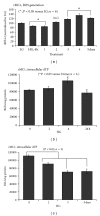
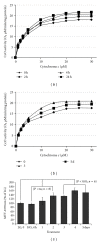
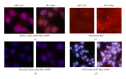
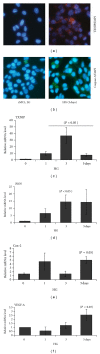
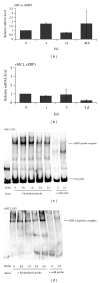
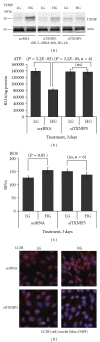
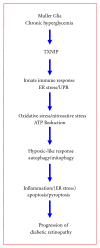
Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP) mediates retinal inflammation, gliosis, and apoptosis in experimental diabetes. Here, we investigate the temporal response of Muller glia to high glucose (HG) and TXNIP expression using a rat Muller cell line (rMC1) in culture. We examined if HG-induced TXNIP expression evokes host defense mechanisms in rMC1 in response to metabolic abnormalities. HG causes sustained up-regulation of TXNIP (2 h to 5 days), ROS generation, ATP depletion, ER stress, and inflammation. Various cellular defense mechanisms are activated by HG: (i) NLRP3 inflammasome, (ii) ER stress response (sXBP1), (iii) hypoxic-like HIF-1α induction, (iv) autophagy/mitophagy, and (v) apoptosis. We also found in vivo that streptozocin-induced diabetic rats have higher retinal TXNIP and innate immune response gene expression than normal rats. Knock down of TXNIP by intravitreal siRNA reduces inflammation (IL-1β) and gliosis (GFAP) in the diabetic retina. TXNIP ablation in vitro prevents ROS generation, restores ATP level and autophagic LC3B induction in rMC1. Thus, our results show that HG sustains TXNIP up-regulation in Muller glia and evokes a program of cellular defense/survival mechanisms that ultimately lead to oxidative stress, ER stress/inflammation, autophagy and apoptosis. TXNIP is a potential target to ameliorate blinding ocular complications of diabetic retinopathy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Critical role of TXNIP in oxidative stress, DNA damage and retinal pericyte apoptosis under high glucose: implications for diabetic retinopathy.Exp Cell Res. 2013 Apr 15;319(7):1001-12. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.01.012. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23353834 Free PMC article.
-
TXNIP regulates mitophagy in retinal Müller cells under high-glucose conditions: implications for diabetic retinopathy.Cell Death Dis. 2017 May 11;8(5):e2777. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.190. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28492550 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Combination Drug Therapy to Prevent Redox Stress and Mitophagy Dysregulation in Retinal Müller Cells under High Glucose Conditions: Implications for Diabetic Retinopathy.Diseases. 2021 Dec 14;9(4):91. doi: 10.3390/diseases9040091. Diseases. 2021. PMID: 34940029 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin-interacting protein in diabetic retinal neurodegeneration: A novel potential therapeutic target for diabetic retinopathy.Front Neurosci. 2022 Aug 9;16:957667. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.957667. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36017183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TXNIP inhibition in the treatment of diabetes. Verapamil as a novel therapeutic modality in diabetic patients.Med Pharm Rep. 2022 Jul;95(3):243-250. doi: 10.15386/mpr-2187. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Med Pharm Rep. 2022. PMID: 36060506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Marker GRP78 in the Normal Retina and Retinal Degeneration Induced by Blue LED Stimuli in Mice.Cells. 2021 Apr 23;10(5):995. doi: 10.3390/cells10050995. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33922686 Free PMC article.
-
TXNIP/TBP-2: A Master Regulator for Glucose Homeostasis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Aug 18;9(8):765. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080765. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32824669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Txnip in Mitophagy Dysregulation and Inflammasome Activation in Diabetic Retinopathy: A New Perspective.JOJ Ophthalmol. 2017;4(4):10.19080/jojo.2017.04.555643. doi: 10.19080/jojo.2017.04.555643. Epub 2017 Sep 15. JOJ Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 29376145 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Molecular Chaperones Improves Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and Decreases the Inflammatory Transcriptome in Diabetic Sensory Neurons.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Sep 16;6(9):1637-48. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00165. Epub 2015 Jul 22. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26161583 Free PMC article.
-
Dorzolamide synergizes the antitumor activity of mitomycin C against Ehrlich's carcinoma grown in mice: role of thioredoxin-interacting protein.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;388(12):1271-82. doi: 10.1007/s00210-015-1163-9. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26264806
References
-
- Cheung N, Mitchell P, Wong TY. Diabetic retinopathy. The Lancet. 2010;376(9735):124–136. - PubMed
-
- Frey T, Antonetti DA. Alterations to the blood-retinal barrier in diabetes: cytokines and reactive oxygen species. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling. 2011;15(5):1271–1284. - PubMed
-
- Xu H, Chen M, Forrester JV. Para-inflammation in the aging retina. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research. 2009;28(5):348–368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
