Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: possible involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress?
- PMID: 22474423
- PMCID: PMC3299342
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/481840
Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: possible involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress?
Abstract
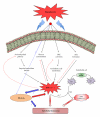
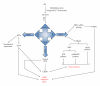
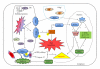
The vascular complications of diabetes mellitus impose a huge burden on the management of this disease. The higher incidence of cardiovascular complications and the unfavorable prognosis among diabetic individuals who develop such complications have been correlated to the hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and associated endothelial dysfunction. Although antioxidants may be considered as effective therapeutic agents to relieve oxidative stress and protect the endothelium, recent clinical trials involving these agents have shown limited therapeutic efficacy in this regard. In the recent past experimental evidence suggest that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in the endothelial cells might be an important contributor to diabetes-related vascular complications. The current paper contemplates the possibility of the involvement of ER stress in endothelial dysfunction and diabetes-associated vascular complications.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization, Bode CD. Media Centre-Fact Sheets, Diabetes, 2011, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/index.html.
-
- Schalkwijk CG, Stehouwer CDA. Vascular complications in diabetes mellitus: the role of endothelial dysfunction. Clinical Science. 2005;109(2):143–159. - PubMed
-
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clinical Diabetes. 2008;26(2):77–82.
-
- Grundy SM, Howard B, Smith S, Jr., Eckel R, Redberg R, Bonow RO. Prevention conference VI: diabetes and cardiovascular disease—executive summary: conference proceeding for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2002;105(18):2231–2239. - PubMed
-
- Bakker W, Eringa EC, Sipkema P, Van Hinsbergh VWM. Endothelial dysfunction and diabetes: roles of hyperglycemia, impaired insulin signaling and obesity. Cell and Tissue Research. 2009;335(1):165–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
