Modulation of lipid metabolism by mixtures of protamine and chitooligosaccharide through pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity in a rat model
- PMID: 22474472
- PMCID: PMC3315200
- DOI: 10.5625/lar.2012.28.1.31
Modulation of lipid metabolism by mixtures of protamine and chitooligosaccharide through pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity in a rat model
Abstract
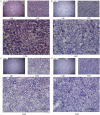
Overweight and obesity are usually related with high fat and calorie intake, and seriously causative of lifestyle-related diseases such as cardiovascular disorders, arteriosclerosis, and colon cancer. In this study, we propose a novel dietary therapy against overweight and obesity using mixtures of protamine and chitooligosaccharide (COS), which are known to interrupt the lipid metabolism in the body. Protamine is a dietary protein originated from salmon reproductive organ, and COS is an oligosaccharide made from chitin or chitosan by chemical or enzymatic hydrolysis. In the enzyme activity analysis in vitro, protamine and COS strongly suppressed the activity of pancreatic lipase, which is the primary enzyme for the digestion and absorption of lipids in the intestine. In in vivo animal test, the mixtures of protamine and COS significantly reduced the serum levels of triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (T-CHO), and low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDLC) and inhibited the accumulation of lipids in liver tissue of Sprague Dawley (SD) rats fed high fat diets. On the other hand, they increased fecal TG and T-CHO contents. From these alterations in lipid metabolism, we verified that protamine and COS mixtures could effectively interrupt the digestion and absorption of dietary lipids in the body by inhibiting pancreatic lipase activity. In addition, protamine and COS mixtures increased the serum level of high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDLC), responsible for removing cholesterol from cells and protecting atherosclerosis, and therefore decreased the potential risks of cardiovascular diseases by lowering values of the atherogenic index (AI) and cardiac risk factor (CRF). Taken together, we suggest protamine and COS mixtures as a prominent dietary therapy for the prevention of overweight, obesity, and further cardiovascular diseases related with hyperlipidemia.
Keywords: Protamine; chitooligosaccharide; cholesterol; high fat diet; triglyceride.
Figures
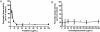
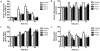
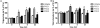
Similar articles
-
Risk of cardiovascular disease is suppressed by dietary supplementation with protamine and chitooligosaccharide in Sprague-Dawley rats.Mol Med Rep. 2013 Jan;7(1):127-33. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.1128. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Mol Med Rep. 2013. PMID: 23064235
-
Salmon Protamine Decreases Serum and Liver Lipid Contents by Inhibiting Lipid Absorption in an In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion Model and in Rats.J Food Sci. 2015 Oct;80(10):H2346-53. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13003. Epub 2015 Sep 9. J Food Sci. 2015. PMID: 26352573
-
Chitosan oligosaccharide decreases very-low-density lipoprotein triglyceride and increases high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in high-fat-diet-fed rats.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2011 Sep;236(9):1064-9. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2011.011032. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2011. PMID: 21856756
-
[Lipid-lowering effect and mechanism of Danhong Injection on hyperlipidemia rats based on lipid metabolism disorder].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Jul;45(13):3203-3210. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200212.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32726030 Chinese.
-
Inhibition of pancreatic lipase, α-glucosidase, α-amylase, and hypolipidemic effects of the total flavonoids from Nelumbo nucifera leaves.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Aug 26;149(1):263-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.034. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23811214
Cited by
-
Dynamic changes of early-stage aortic lipid deposition in chronic renal failure rats and effects of decorin gene therapy.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Feb;9(2):591-597. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.2106. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 25574240 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan Oligosaccharide Inhibits the Synthesis of Milk Fat in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells through AMPK-Mediated Downstream Signaling Pathway.Animals (Basel). 2022 Jun 30;12(13):1692. doi: 10.3390/ani12131692. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35804595 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional factors affecting abdominal fat deposition in poultry: a review.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2014 Jul;27(7):1057-68. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2013.13702. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2014. PMID: 25050050 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Chitosan Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Inflammation in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) through Regulation of Nrf2/Kaep1 and Bcl-2/Bax Pathways.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jun 30;13(7):486. doi: 10.3390/biology13070486. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056682 Free PMC article.
-
Theophylline Extracted from Fu Brick Tea Affects the Metabolism of Preadipocytes and Body Fat in Mice as a Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitor.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 25;23(5):2525. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052525. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pokorski R. Effect of increasing body weight on morbidity and mortality in South Korea. J Insur Med. 2011;42(2-4):78–84. - PubMed
-
- Aspedon A, Groisman EA. The antibacterial action of protamine: evidence for disruption of cytoplasmic membrane energization in Salmonella typhimurium. Microbiology. 1996;142(Pt 12):3389–3397. - PubMed
-
- Duarte-Vázquez MA, García-Padilla S, Olvera-Ochoa L, González-Romero KE, Acosta-Iñiguez J, De la Cruz-Cordero R, Rosado JL. Effect of protamine in obesity induced by high-fat diets in rats. Int J Obes (Lond) 2009;33(6):687–692. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

