Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Effects of Labisia pumila Ethanol Extract and Its Active Fraction in Human Melanoma HM3KO Cells
- PMID: 22474490
- PMCID: PMC3310196
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/123470
Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Effects of Labisia pumila Ethanol Extract and Its Active Fraction in Human Melanoma HM3KO Cells
Abstract
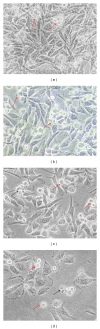
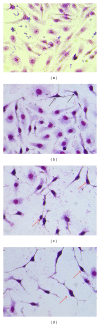
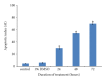
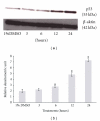
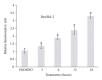
The present study was to determine the anticancer potential of Labisia pumila in in vitro models. Results from the study revealed that ethanol extract of L. pumila was more cytotoxic against HM3KO cells while having reduced effects on nonmalignant cells as compared to aqueous and hexane extracts. Thus, ethanol extract was selected to be further separated by using the bioassay-guided fractionation method to give an active fraction, SF2Lp. Results obtained from the flow cytometry analysis showed that SF2Lp was able to arrest the HM3KO cell cycle at the G1 phase, while morphological findings from AO-EB nuclear staining assays along with the Apoptotic Index confirmed the induction of apoptosis by SF2Lp in HM3KO cells. Results from the mechanistic study further revealed that SF2Lp treatment was able to concurrently increase the expression level of p53 and pro-apoptotic protein Bax and also reduce the expression level of anti-apoptotic protein BCl-2 in HM3KO cells, directly contributing to the increase in Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. These findings, therefore, suggested that L. pumila was able to inhibit HM3KO cell growth possibly by arresting the cell cycle at G1 phase and inducing apoptosis in HM3KO cells via the up- and down-regulation of Bax/Bcl-2 protein, mediated through a p53-dependent pathway.
Figures





References
-
- Lee HJ, Lee EO, Rhee YH, et al. An oriental herbal cocktail, ka-mi-kae-kyuk-tang, exerts anti-cancer activities by targeting angiogenesis, apoptosis and metastasis. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27(12):2455–2463. - PubMed
-
- Issa AY, Volate SR, Wargovich MJ. The role of phytochemicals in inhibition of cancer and inflammation: new directions and perspectives. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. 2006;19(5):405–419.
-
- Cragg GM, Newman DJ. Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2005;100(1-2):72–79. - PubMed
-
- Jordan MA, Wilson L. Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2004;4(4):253–265. - PubMed
-
- Lowe SW, Lin AW. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21(3):485–495. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

