Modified huo-luo-xiao-ling dan suppresses adjuvant arthritis by inhibiting chemokines and matrix-degrading enzymes
- PMID: 22474510
- PMCID: PMC3310235
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/589256
Modified huo-luo-xiao-ling dan suppresses adjuvant arthritis by inhibiting chemokines and matrix-degrading enzymes
Abstract
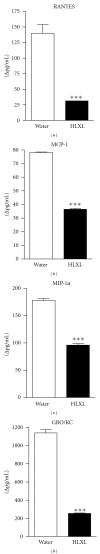
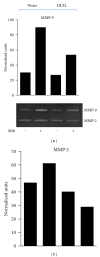
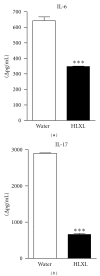
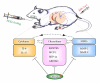
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the joints that can lead to deformities and disability. The prolonged use of conventionally used drugs is associated with severe adverse reactions. Therefore, safer and less expensive therapeutic products are continually being sought. Huo-Luo-Xiao-Ling dan (HLXL), a traditional Chinese herbal mixture, and its modified versions possess anti-arthritic activity. In this paper, we examined the influence of modified HLXL on two of the key mediators of arthritic inflammation and tissue damage, namely, chemokines and matrix-metalloproteinases (MMPs) in the rat adjuvant-induced arthritis (AA) model of RA. We treated arthritic Lewis rats with HLXL (2.3 g/kg) by daily gavage beginning at the onset of AA. The control rats received the vehicle. At the peak phase of AA, rats were sacrificed and their draining lymph node cells (LNC) and spleen adherent cells (SAC) were tested. The HLXL-treated rats showed a significant reduction in the levels of chemokines (RANTES, MCP-1, MIP-1α, and GRO/KC), MMPs (MMP 2 and 9), as well as cytokines (IL-6 and IL-17) that induce them, compared to the control vehicle-treated rats. Thus, HLXL controls arthritis in part by suppressing the mediators of immune pathology, and it might offer a promising alternative/adjunct treatment for RA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chinese Herbal Formula Huo-Luo-Xiao-Ling Dan Protects against Bone Damage in Adjuvant Arthritis by Modulating the Mediators of Bone Remodeling.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:429606. doi: 10.1155/2013/429606. Epub 2013 May 16. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23762133 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray analysis reveals the molecular basis of antiarthritic activity of huo-luo-xiao-ling dan.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:524746. doi: 10.1155/2013/524746. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23983789 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of ongoing experimental arthritis by a chinese herbal formula (huo-luo-xiao-ling dan) involves changes in antigen-induced immunological and biochemical mediators of inflammation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:642027. doi: 10.1155/2011/642027. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. PMID: 20981317 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of autoimmune arthritis by Celastrus-derived Celastrol through modulation of pro-inflammatory chemokines.Bioorg Med Chem. 2012 Sep 1;20(17):5229-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.06.050. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22854193 Free PMC article.
-
Control of autoimmune inflammation by celastrol, a natural triterpenoid.Pathog Dis. 2016 Aug;74(6):ftw059. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw059. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Pathog Dis. 2016. PMID: 27405485 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chinese Herbal Formula Huo-Luo-Xiao-Ling Dan Protects against Bone Damage in Adjuvant Arthritis by Modulating the Mediators of Bone Remodeling.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:429606. doi: 10.1155/2013/429606. Epub 2013 May 16. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23762133 Free PMC article.
-
Mediators of inflammation-induced bone damage in arthritis and their control by herbal products.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:518094. doi: 10.1155/2013/518094. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23476694 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics and interplay of mediators of inflammation-induced bone damage in the course of adjuvant arthritis.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2013 Jan-Mar;26(1):37-48. doi: 10.1177/039463201302600104. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23527707 Free PMC article.
-
A computational and functional study elicits the ameliorating effect of the Chinese herbal formula Huo Luo Xiao Ling Dan on experimental ischemia-induced myocardial injury in rats via inhibition of apoptosis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Feb 18;9:1063-102. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S76336. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25733819 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray analysis reveals the molecular basis of antiarthritic activity of huo-luo-xiao-ling dan.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:524746. doi: 10.1155/2013/524746. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23983789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lipsky PE. Rheumatoid arthritis. In: Fauci A, Braunwald E, Kasper D, et al., editors. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 17th edition. New York, NY, USA: McGraw Hil; 2008. pp. 2083–2092.
-
- FitzGerald GA. Coxibs and cardiovascular disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2004;351(17):1709–1711. - PubMed
-
- Scheiman JM. The impact of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastropathy. The American Journal of Managed Care. 2001;7(1, supplement):S10–S14. - PubMed
-
- Taibi DM, Bourguignon C. The role of complementary and alternative therapies in managing rheumatoid arthritis. Family & Community Health. 2003;26(1):41–52. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

