Portulaca oleracea Ameliorates Diabetic Vascular Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction in db/db Mice
- PMID: 22474522
- PMCID: PMC3303738
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/741824
Portulaca oleracea Ameliorates Diabetic Vascular Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction in db/db Mice
Abstract
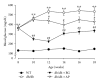
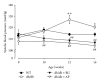
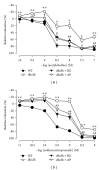
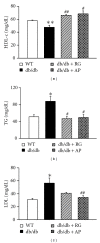
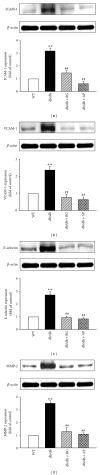
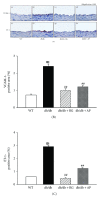
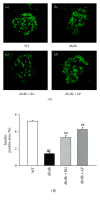
Type 2 diabetes is associated with significantly accelerated rates of micro- and macrovascular complications such as diabetic vascular inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. In the present study, we investigated the protective effect of the aqueous extract of Portulaca oleracea L. (AP), an edible plant used as a folk medicine, on diabetic vascular complications. The db/db mice were treated with AP (300 mg/kg/day, p.o.) for 10 weeks, and AP treatment markedly lowered blood glucose, plasma triglyceride, plasma level of LDL-cholesterol, and systolic blood pressure in diabetic db/db mice. Furthermore, AP significantly increased plasma level of HDL-cholesterol and insulin level. The impairment of ACh- and SNP-induced vascular relaxation of aortic rings were ameliorated by AP treatment in diabetic db/db mice. This study also showed that overexpression of VCAM-1, ICAM-1, E-selectin, MMP-2, and ET-1 were observed in aortic tissues of untreated db/db mice, which were significantly suppressed by treatment with AP. We also found that the insulin immunoreactivity of the pancreatic islets remarkably increased in AP treated db/db mice compared with untreated db/db mice. Taken together, AP suppresses hyperglycemia and diabetic vascular inflammation, and prevents the development of diabetic endothelial dysfunction for the development of diabetes and its vascular complications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An aqueous extract of Portulaca oleracea ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through suppression of renal fibrosis and inflammation in diabetic db/db mice.Am J Chin Med. 2012;40(3):495-510. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X12500383. Am J Chin Med. 2012. PMID: 22745066
-
Anti-diabetic atherosclerosis effect of Prunella vulgaris in db/db mice with type 2 diabetes.Am J Chin Med. 2012;40(5):937-51. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X12500693. Am J Chin Med. 2012. PMID: 22928826
-
Impairment of endothelium-dependent ACh-induced relaxation in aorta of diabetic db/db mice--possible dysfunction of receptor and/or receptor-G protein coupling.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;377(4-6):401-10. doi: 10.1007/s00210-008-0261-3. Epub 2008 Jan 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18228001
-
Resveratrol ameliorates diabetic vascular inflammation and macrophage infiltration in db/db mice by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway.Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2014 Mar;11(2):92-102. doi: 10.1177/1479164113520332. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2014. PMID: 24464099
-
Arctium lappa ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in rats fed with high fat/cholesterol diets.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012 Aug 6;12:116. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-116. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012. PMID: 22866890 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Portulaca Oleracea L. (Purslane) Extract Protects Endothelial Function by Reducing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Oxidative Stress through AMPK Activation in Diabetic Obese Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 18;12(12):2132. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122132. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136251 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Effects of Portulaca Oleracea Seeds on Dyslipidemia in Obese Adolescents: a Triple-blinded Randomized Controlled Trial.Med Arch. 2014 Jun;68(3):195-9. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2014.68.195-199. Epub 2014 May 31. Med Arch. 2014. PMID: 25568533 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phytochemical Characteristics and Anti-Inflammatory, Immunoregulatory, and Antioxidant Effects of Portulaca oleracea L.: A Comprehensive Review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Aug 31;2023:2075444. doi: 10.1155/2023/2075444. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37693918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Portulaca oleracea L.: a review of phytochemistry and pharmacological effects.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:925631. doi: 10.1155/2015/925631. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25692148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of Portulaca oleracea and α-linolenic acid on oxidant/antioxidant biomarkers of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Indian J Pharmacol. 2018 Jul-Aug;50(4):177-184. doi: 10.4103/ijp.IJP_737_16. Indian J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30505053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Libby P, Plutzky J. Diabetic macrovascular disease: the glucose paradox? Circulation. 2002;106(22):2760–2763. - PubMed
-
- Mokdad AH, Bowman BA, Ford ES, Vinicor F, Marks JS, Koplan JP. The continuing epidemics of obesity and diabetes in the United States. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2001;286(10):1195–1200. - PubMed
-
- Chakir M, Plante GE. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Prostaglandins Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids. 1996;54(1):45–51. - PubMed
-
- Harris AK, Hutchinson JR, Sachidanandam K, et al. Type 2 diabetes causes remodeling of cerebrovasculature via differential regulation of matrix metalloproteinases and collagen synthesis: role of endothelin-1. Diabetes. 2005;54(9):2638–2644. - PubMed
-
- Ammarguellat FZ, Gannon PO, Amiri F, Schiffrin EL. Fibrosis, matrix metalloproteinases, and inflammation in the heart of DOCA-salt hypertensive rats: role of ETa receptors. Hypertension. 2002;39(2):679–684. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

