Antigen targets of type 1 diabetes autoimmunity
- PMID: 22474615
- PMCID: PMC3312399
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007781
Antigen targets of type 1 diabetes autoimmunity
Abstract
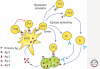
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by recognition of one or more β-cell proteins by the immune system. The list of target antigens in this disease is ever increasing and it is conceivable that additional islet autoantigens, possibly including pivotal β-cell targets, remain to be discovered. Many knowledge gaps remain with respect to the disorder's pathogenesis, including the cause of loss of tolerance to islet autoantigens and an explanation as to why targeting of proteins with a distribution of expression beyond β cells may result in selective β-cell destruction and type 1 diabetes. Yet, our knowledge of β-cell autoantigens has already led to translation into tissue-specific immune intervention strategies that are currently being assessed in clinical trials for their efficacy to halt or delay disease progression to type 1 diabetes, as well as to reverse type 1 diabetes. Here we will discuss recently gained insights into the identity, biology, structure, and presentation of islet antigens in relation to disease heterogeneity and β-cell destruction.
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach P, Bonifacio E, Koczwara K, Ziegler AG 2005. Natural history of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 54 Suppl 2: S25–S31 - PubMed
-
- Anderson MS, Venanzi ES, Klein L, Chen Z, Berzins SP, Turley SJ, von Boehmer H, Bronson R, Dierich A, Benoist C, et al. 2002. Projection of an immunological self shadow within the thymus by the aire protein. Science 298: 1395–1401 - PubMed
-
- Arentz-Hansen H, Körner R, Molberg O, Quarsten H, Vader W, Kooy YM, Lundin KE, Koning F, Roepstorff P, Sollid LM, et al. 2000. The intestinal T cell response to α-gliadin in adult celiac disease is focused on a single deamidated glutamine targeted by tissue transglutaminase. J Exp Med 191: 603–612 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
