Stochastic resonance whole body vibration reduces musculoskeletal pain: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 22474630
- PMCID: PMC3302035
- DOI: 10.5312/wjo.v2.i12.116
Stochastic resonance whole body vibration reduces musculoskeletal pain: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Aim: To examined the effects of stochastic resonance whole-body vibration training on musculoskeletal pain in young healthy individuals.
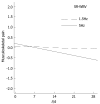
Methods: Participants were 43 undergraduate students of a Swiss University. The study was designed as a randomized controlled trial (RCT) with randomized group allocation. The RCT consisted of two groups each given 12 training sessions during four weeks with either 5 Hz- Training frequency (training condition) or 1.5 Hz Training frequency (control condition). Outcome was current musculoskeletal pain assessed in the evening on each day during the four week training period.
Results: Multilevel regression analysis showed musculoskeletal pain was significantly decreased in the training condition whereas there was no change in the control condition (B = -0.023, SE = 0.010, P = 0.021). Decrease in current musculoskeletal pain over four weeks was linear.
Conclusion: Stochastic resonance whole-body vibration reduced musculoskeletal pain in young healthy individuals. Stochastic resonance vibration and not any other exercise component within training caused pain reduction.
Keywords: Musculoskeletal pain; Randomized controlled trial; Stochastic vibration; Training study.
Figures
References
-
- Schollhorn WI, Beckmann H, Michelbrink M, Sechelmann M, Trockel M, Davids K. Does noise provide a basis for the unification of motor learning theories? Int J Sport Psychol. 2006;37:186–206.
-
- van Nes IJ, Latour H, Schils F, Meijer R, van Kuijk A, Geurts AC. Long-term effects of 6-week whole-body vibration on balance recovery and activities of daily living in the postacute phase of stroke: a randomized, controlled trial. Stroke. 2006;37:2331–2335. - PubMed
-
- Lauper M, Kuhn A, Gerber R, Luginbühl H, Radlinger L. Pelvic floor stimulation: what are the good vibrations? Neurourol Urodyn. 2009;28:405–410. - PubMed
-
- Haas CT, Turbanski S, Kaiser I, Schmidtbleicher D. Biomechanical and physiological effects of oscillating mechanical stimuli in humans. Deutsche Zeitschrift fur Sportmedizin. 2004;55:34–42.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources