Human neuroblastoma cells with acquired resistance to the p53 activator RITA retain functional p53 and sensitivity to other p53 activating agents
- PMID: 22476102
- PMCID: PMC3358013
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2012.35
Human neuroblastoma cells with acquired resistance to the p53 activator RITA retain functional p53 and sensitivity to other p53 activating agents
Abstract
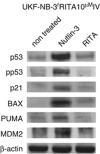
Adaptation of wild-type p53 expressing UKF-NB-3 cancer cells to the murine double minute 2 inhibitor nutlin-3 causes de novo p53 mutations at high frequency (13/20) and multi-drug resistance. Here, we show that the same cells respond very differently when adapted to RITA, a drug that, like nutlin-3, also disrupts the p53/Mdm2 interaction. All of the 11 UKF-NB-3 sub-lines adapted to RITA that we established retained functional wild-type p53 although RITA induced a substantial p53 response. Moreover, all RITA-adapted cell lines remained sensitive to nutlin-3, whereas only five out of 10 nutlin-3-adapted cell lines retained their sensitivity to RITA. In addition, repeated adaptation of the RITA-adapted sub-line UKF-NB-3(r)RITA(10 μM) to nutlin-3 resulted in p53 mutations. The RITA-adapted UKF-NB-3 sub-lines displayed no or less pronounced resistance to vincristine, cisplatin, and irradiation than nutlin-3-adapted UKF-NB-3 sub-lines. Furthermore, adaptation to RITA was associated with fewer changes at the expression level of antiapoptotic factors than observed with adaptation to nutlin-3. Transcriptomic analyses indicated the RITA-adapted sub-lines to be more similar at the gene expression level to the parental UKF-NB-3 cells than nutlin-3-adapted UKF-NB-3 sub-lines, which correlates with the observed chemotherapy and irradiation sensitivity phenotypes. In conclusion, RITA-adapted cells retain functional p53, remain sensitive to nutlin-3, and display a less pronounced resistance phenotype than nutlin-3-adapted cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Adaptation of cancer cells from different entities to the MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 results in the emergence of p53-mutated multi-drug-resistant cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2011 Dec 15;2(12):e243. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.129. Cell Death Dis. 2011. PMID: 22170099 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of the selective MDM2 antagonist nutlin-3 against chemoresistant neuroblastoma with wild-type p53.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009 Nov 18;101(22):1562-74. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp355. Epub 2009 Nov 10. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009. PMID: 19903807
-
Cisplatin in Combination with MDM2 Inhibition Downregulates Rad51 Recombinase in a Bimodal Manner to Inhibit Homologous Recombination and Augment Tumor Cell Kill.Mol Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;97(4):237-249. doi: 10.1124/mol.119.117564. Epub 2020 Feb 16. Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32063580 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the therapeutic perspectives of Nutlin-3.Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(6):569-77. doi: 10.2174/138161211795222586. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 21391907 Review.
-
Deciphering the Role of p53 and TAp73 in Neuroblastoma: From Pathogenesis to Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;14(24):6212. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246212. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Testing of the Survivin Suppressant YM155 in a Large Panel of Drug-Resistant Neuroblastoma Cell Lines.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Mar 2;12(3):577. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030577. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32131402 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-adapted cancer cell lines as preclinical models of acquired resistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2019 Sep 19;2(3):447-456. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2019.005. eCollection 2019. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 35582596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance mechanisms to inhibitors of p53-MDM2 interactions in cancer therapy: can we overcome them?Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2021 Dec 15;26(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s11658-021-00293-6. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34911439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiosensitization of wildtype p53 cancer cells by the MDM2-inhibitor PXN727 is associated with altered heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) levels.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013 Mar;18(2):183-91. doi: 10.1007/s12192-012-0369-8. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013. PMID: 22933182 Free PMC article.
-
Novel MDM2 inhibitor SAR405838 (MI-773) induces p53-mediated apoptosis in neuroblastoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):82757-82769. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12634. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27764791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown CJ, Cheok CF, Verma CS, Lane DP. Reactivation of p53: from peptides to small molecules. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011;32:53–62. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Ahmed A, Poon E, Perusinghe N, de Haven Brandon A, Box G, et al. Small-molecule activation of p53 blocks hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in vivo and leads to tumor cell apoptosis in normoxia and hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:2243–2253. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

