HIV infection and antiretroviral therapy have divergent effects on mitochondria in adipose tissue
- PMID: 22476717
- PMCID: PMC3357134
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis101
HIV infection and antiretroviral therapy have divergent effects on mitochondria in adipose tissue
Abstract
Background: Although human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and antiretroviral therapy (ART) affect mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) content and function, comprehensive evaluations of their effects on mitochondria in muscle, adipose tissue, and blood cells are limited.
Methods: Mitochondrial DNA quantification, mitochondrial genome sequencing, and gene expression analysis were performed on muscle, adipose tissue, and peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) samples from untreated HIV-positive patients, HIV-positive patients receiving nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)-based ART, and HIV-negative controls.
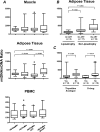
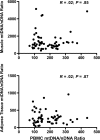
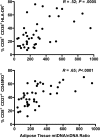
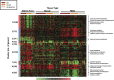
Results: The adipose tissue mtDNA/nuclear DNA (nDNA) ratio was increased in untreated HIV-infected patients (ratio, 353) and decreased in those receiving ART (ratio, 162) compared with controls (ratio, 255; P < .05 for both comparisons); the difference between the 2 HIV-infected groups was also significant (P = .002). In HIV-infected participants, mtDNA/nDNA in adipose tissue correlated with the level of activation (CD38+ /HLA-DR+) for CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes. No significant differences in mtDNA content were noted in muscle or PMBCs among groups. Exploratory DNA microarray analysis identified differential gene expression between patient groups, including a subset of adipose tissue genes.
Conclusions: HIV infection and ART have opposing effects on mtDNA content in adipose tissue; immune activation may mediate the effects of HIV, whereas NRTIs likely mediate the effects of ART.
Figures

Comment in
-
HIV and mitochondria: more than just drug toxicity.J Infect Dis. 2012 Jun 15;205(12):1769-71. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis105. Epub 2012 Apr 3. J Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22476715 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services; 2011. pp. 1–166. http://www.aidsinfo.nih.gov/ContentFiles/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. Accessed 13 January 2011.
-
- Chen CH, Cheng YC. Delayed cytotoxicity and selective loss of mitochondrial DNA in cells treated with the anti-human immunodeficiency virus compound 2′,3′-dideoxycytidine. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:11934–7. - PubMed
-
- Chen CH, Vazquez-Padua M, Cheng YC. Effect of anti-human immunodeficiency virus nucleoside analogs on mitochondrial DNA and its implication for delayed toxicity. Mol Pharmacol. 1991;39:625–8. - PubMed
-
- Brinkman K, ter Hofstede HJ, Burger DM, Smeitink JA, Koopmans PP. Adverse effects of reverse transcriptase inhibitors: mitochondrial toxicity as common pathway. AIDS. 1998;12:1735–44. - PubMed
-
- Lewis W, Dalakas MC. Mitochondrial toxicity of antiviral drugs. Nat Med. 1995;1:417–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

