The mammalian circadian system is resistant to dioxin
- PMID: 22476776
- PMCID: PMC3337685
- DOI: 10.1177/0748730411434405
The mammalian circadian system is resistant to dioxin
Abstract
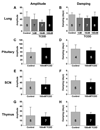
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-dependent transcription factor that is bound and activated by many toxic ubiquitous environmental contaminants, including the halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). The AhR belongs to a family of proteins that contain basic helix-loop-helix/Per-ARNT-SIM (bHLH/PAS) domains. The circadian clock protein, BMAL1, is also a bHLH-PAS transcription factor and has been shown to interact with the AhR. AhRs are expressed in nearly every mammalian tissue, including the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), and previous studies have suggested that activation of the AhR with dioxins affects rhythmicity in circadian clocks. In this study, the authors tested the hypothesis that activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor with the potent dioxin, TCDD, alters the organization of the mammalian circadian system by measuring bioluminescence from tissues explanted from PER2::LUCIFERASE mice. They found that in vitro treatment of explanted tissues with TCDD did not alter the periods, amplitudes, or damping rates of the PER2::LUC rhythms compared with controls. Likewise, in vivo treatment with TCDD had no effect on the phase relationship between central and peripheral oscillators. Together, these data demonstrate that activation of the AhR with TCDD does not directly or systemically alter the mouse circadian system.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) have no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circadian clock disruption in the mouse ovary in response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.Toxicol Lett. 2011 Mar 5;201(2):116-22. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.12.013. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Toxicol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21182907 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral rhythmicity of mice lacking AhR and attenuation of light-induced phase shift by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.J Biol Rhythms. 2008 Jun;23(3):200-10. doi: 10.1177/0748730408316022. J Biol Rhythms. 2008. PMID: 18487412 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression and activity in cerebellar granule neuroblasts: implications for development and dioxin neurotoxicity.Toxicol Sci. 2005 Feb;83(2):340-8. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi031. Epub 2004 Nov 10. Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15537747
-
Mechanisms of ligand-induced aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated biochemical and toxic responses.Toxicol Pathol. 1998 Sep-Oct;26(5):657-71. doi: 10.1177/019262339802600510. Toxicol Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9789953 Review.
-
Crosstalk between the AHR signaling pathway and circadian rhythm.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Feb 15;77(4):560-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.09.040. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18983986 Review.
Cited by
-
High-fat diet acutely affects circadian organisation and eating behavior.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Apr;37(8):1350-6. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12133. Epub 2013 Jan 21. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23331763 Free PMC article.
-
Wheel-running activity modulates circadian organization and the daily rhythm of eating behavior.Front Psychol. 2014 Mar 4;5:177. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00177. eCollection 2014. Front Psychol. 2014. PMID: 24624109 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Dioxin-mediated signaling and circadian clock: a possible determinant in metabolic homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Jul 1;15(7):11700-12. doi: 10.3390/ijms150711700. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24987953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian Regulation of Benzo[a]Pyrene Metabolism and DNA Adduct Formation in Breast Cells and the Mouse Mammary Gland.Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;91(3):178-188. doi: 10.1124/mol.116.106740. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28007926 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation at AHRR as a master predictor of smoke exposure and a biomarker for sleep and exercise.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Oct 18;16(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01757-0. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 39425209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott BD, Birnbaum LS, Perdew GH. Developmental expression of two members of a new class of transcription factors: I. Expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the C57BL/6N mouse embryo. Dev Dyn. 1995;204:133–143. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Salguero P, Pineau T, Hilbert DM, McPhail T, Lee SS, Kimura S, Nebert DW, Rudikoff S, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ. Immune system impairment and hepatic fibrosis in mice lacking the dioxin-binding Ah receptor. Science. 1995;268:722–726. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Salguero PM, Hilbert DM, Rudikoff S, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ. Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice are resistant to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1996;140:173–179. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Salguero PM, Ward JM, Sundberg JP, Gonzalez FJ. Lesions of aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice. Vet Pathol. 1997;34:605–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

