The antihypertensive effect of cysteine
- PMID: 22477470
- PMCID: PMC2721729
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0031-1278316
The antihypertensive effect of cysteine
Abstract
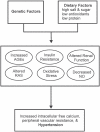
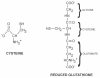
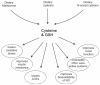
Hypertension is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Individuals with hypertension are at an increased risk for stroke, heart disease and kidney failure. Essential hypertension results from a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. One such lifestyle factor is diet, and its role in the control of blood pressure has come under much scrutiny. Just as increased salt and sugar are known to elevate blood pressure, other dietary factors may have antihypertensive effects. Studies including the Optimal Macronutrient Intake to Prevent Heart Disease (OmniHeart) study, Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT), International Study of Salt and Blood Pressure (INTERSALT) and Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) study have demonstrated an inverse relationship between dietary protein and blood pressure. One component of dietary protein that may partially account for its antihypertensive effect is the nonessential amino acid cysteine. Studies in hypertensive humans and animal models of hypertension have shown that N-acetylcysteine, a stable cysteine analogue, lowers blood pressure, which substantiates this idea. Cysteine may exert its antihypertensive effects directly or through its storage form, glutathione, by decreasing oxidative stress, improving insulin resistance and glucose metabolism, lowering advanced glycation end products, and modulating levels of nitric oxide and other vasoactive molecules. Therefore, adopting a balanced diet containing cysteine-rich proteins may be a beneficial lifestyle choice for individuals with hypertension. An example of such a diet is the DASH diet, which is low in salt and saturated fat; includes whole grains, poultry, fish and nuts; and is rich in vegetables, fruits and low-fat dairy products.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Global strategy on diet, physical activity and health. Chronic disease risk factors. < www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/publications/facts/riskfactors/en> (Version current at May 1, 2009).
-
- Ferrannini E, Buzzigoli G, Bonadonna R, et al. Insulin resistance in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:350–7. - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM. Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and hypertriglyceridemia in the etiology and clinical course of hypertension. Am J Med. 1991;90:7S–12S. - PubMed
-
- Sagar S, Kallo IJ, Kaul N, Ganguly NK, Sharma BK. Oxygen free radicals in essential hypertension. Mol Cell Biochem. 1992;111:103–8. - PubMed
-
- Kumar KV, Das UN. Are free radicals involved in the pathobiology of human essential hypertension? Free Radic Res Commun. 1993;19:59–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

