Igf1r signaling is indispensable for preimplantation development and is activated via a novel function of E-cadherin
- PMID: 22479204
- PMCID: PMC3315466
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002609
Igf1r signaling is indispensable for preimplantation development and is activated via a novel function of E-cadherin
Abstract
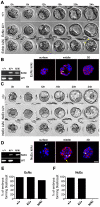
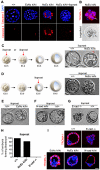
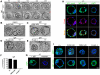
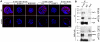
Insulin-like growth factor I receptor (Igf1r) signaling controls proliferation, differentiation, growth, and cell survival in many tissues; and its deregulated activity is involved in tumorigenesis. Although important during fetal growth and postnatal life, a function for the Igf pathway during preimplantation development has not been described. We show that abrogating Igf1r signaling with specific inhibitors blocks trophectoderm formation and compromises embryo survival during murine blastocyst formation. In normal embryos total Igf1r is present throughout the membrane, whereas the activated form is found exclusively at cell contact sites, colocalizing with E-cadherin. Using genetic domain switching, we show a requirement for E-cadherin to maintain proper activation of Igf1r. Embryos expressing exclusively a cadherin chimera with N-cadherin extracellular and E-cadherin intracellular domains (NcEc) fail to form a trophectoderm and cells die by apoptosis. In contrast, homozygous mutant embryos expressing a reverse-structured chimera (EcNc) show trophectoderm survival and blastocoel cavitation, indicating a crucial and non-substitutable role of the E-cadherin ectodomain for these processes. Strikingly, blastocyst formation can be rescued in homozygous NcEc embryos by restoring Igf1r signaling, which enhances cell survival. Hence, perturbation of E-cadherin extracellular integrity, independent of its cell-adhesion function, blocked Igf1r signaling and induced cell death in the trophectoderm. Our results reveal an important and yet undiscovered function of Igf1r during preimplantation development mediated by a unique physical interaction between Igf1r and E-cadherin indispensable for proper receptor activation and anti-apoptotic signaling. We provide novel insights into how ligand-dependent Igf1r activity is additionally gated to sense developmental potential in utero and into a bifunctional role of adhesion molecules in contact formation and signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


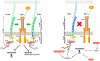
References
-
- Rossant J, Tam PP. Blastocyst lineage formation, early embryonic asymmetries and axis patterning in the mouse. Development. 2009;136:701–713. - PubMed
-
- Chazaud C, Yamanaka Y, Pawson T, Rossant J. Early lineage segregation between epiblast and primitive endoderm in mouse blastocysts through the Grb2-MAPK pathway. Dev Cell. 2006;10:615–624. - PubMed
-
- Nichols J, Zevnik B, Anastassiadis K, Niwa H, Klewe-Nebenius D, et al. Formation of pluripotent stem cells in the mammalian embryo depends on the POU transcription factor Oct4. Cell. 1998;95:379–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

