Metabolic profiling of a mapping population exposes new insights in the regulation of seed metabolism and seed, fruit, and plant relations
- PMID: 22479206
- PMCID: PMC3315483
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002612
Metabolic profiling of a mapping population exposes new insights in the regulation of seed metabolism and seed, fruit, and plant relations
Abstract
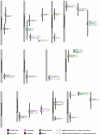
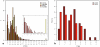
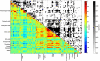
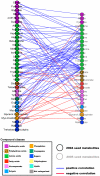
To investigate the regulation of seed metabolism and to estimate the degree of metabolic natural variability, metabolite profiling and network analysis were applied to a collection of 76 different homozygous tomato introgression lines (ILs) grown in the field in two consecutive harvest seasons. Factorial ANOVA confirmed the presence of 30 metabolite quantitative trait loci (mQTL). Amino acid contents displayed a high degree of variability across the population, with similar patterns across the two seasons, while sugars exhibited significant seasonal fluctuations. Upon integration of data for tomato pericarp metabolite profiling, factorial ANOVA identified the main factor for metabolic polymorphism to be the genotypic background rather than the environment or the tissue. Analysis of the coefficient of variance indicated greater phenotypic plasticity in the ILs than in the M82 tomato cultivar. Broad-sense estimate of heritability suggested that the mode of inheritance of metabolite traits in the seed differed from that in the fruit. Correlation-based metabolic network analysis comparing metabolite data for the seed with that for the pericarp showed that the seed network displayed tighter interdependence of metabolic processes than the fruit. Amino acids in the seed metabolic network were shown to play a central hub-like role in the topology of the network, maintaining high interactions with other metabolite categories, i.e., sugars and organic acids. Network analysis identified six exceptionally highly co-regulated amino acids, Gly, Ser, Thr, Ile, Val, and Pro. The strong interdependence of this group was confirmed by the mQTL mapping. Taken together these results (i) reflect the extensive redundancy of the regulation underlying seed metabolism, (ii) demonstrate the tight co-ordination of seed metabolism with respect to fruit metabolism, and (iii) emphasize the centrality of the amino acid module in the seed metabolic network. Finally, the study highlights the added value of integrating metabolic network analysis with mQTL mapping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Schauer N, Semel Y, Roessner U, Gur A, Balbo I, et al. Comprehensive metabolic profiling and phenotyping of interspecific introgression lines for tomato improvement. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:447–454. - PubMed
-
- Moftah AE, Al-Redhaiman KN. Effects of preharvest foliar spray of ‘Limewash’ on water relations, quantity, quality, and shelf life of bell pepper under water deficit conditions. Eur J Hortic Sci. 2006;71:78–83.
-
- Gilbert L, Alhagdow M, Nunes-Nesi A, Quemener B, Guillon F, et al. GDP-d-mannose 3,5-epimerase (GME) plays a key role at the intersection of ascorbate and non-cellulosic cell-wall biosynthesis in tomato. Plant J. 2009;60:499–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

