GPS-ARM: computational analysis of the APC/C recognition motif by predicting D-boxes and KEN-boxes
- PMID: 22479614
- PMCID: PMC3315528
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034370
GPS-ARM: computational analysis of the APC/C recognition motif by predicting D-boxes and KEN-boxes
Abstract
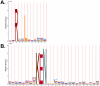
Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), an E3 ubiquitin ligase incorporated with Cdh1 and/or Cdc20 recognizes and interacts with specific substrates, and faithfully orchestrates the proper cell cycle events by targeting proteins for proteasomal degradation. Experimental identification of APC/C substrates is largely dependent on the discovery of APC/C recognition motifs, e.g., the D-box and KEN-box. Although a number of either stringent or loosely defined motifs proposed, these motif patterns are only of limited use due to their insufficient powers of prediction. We report the development of a novel GPS-ARM software package which is useful for the prediction of D-boxes and KEN-boxes in proteins. Using experimentally identified D-boxes and KEN-boxes as the training data sets, a previously developed GPS (Group-based Prediction System) algorithm was adopted. By extensive evaluation and comparison, the GPS-ARM performance was found to be much better than the one using simple motifs. With this powerful tool, we predicted 4,841 potential D-boxes in 3,832 proteins and 1,632 potential KEN-boxes in 1,403 proteins from H. sapiens, while further statistical analysis suggested that both the D-box and KEN-box proteins are involved in a broad spectrum of biological processes beyond the cell cycle. In addition, with the co-localization information, we predicted hundreds of mitosis-specific APC/C substrates with high confidence. As the first computational tool for the prediction of APC/C-mediated degradation, GPS-ARM is a useful tool for information to be used in further experimental investigations. The GPS-ARM is freely accessible for academic researchers at: http://arm.biocuckoo.org.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Milestones in cell division. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:E265. - PubMed
-
- Nasmyth K. A prize for proliferation. Cell. 2001;107:689–701. - PubMed
-
- Barford D. Structure, function and mechanism of the anaphase promoting complex (APC/C). Q Rev Biophys. 2011;44:153–190. - PubMed
-
- Thornton BR, Toczyski DP. Precise destruction: an emerging picture of the APC. Genes Dev. 2006;20:3069–3078. - PubMed
-
- Peters JM. The anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome: a machine designed to destroy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:644–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

