A "Copernican" reassessment of the human mitochondrial DNA tree from its root
- PMID: 22482806
- PMCID: PMC3322232
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.03.002
A "Copernican" reassessment of the human mitochondrial DNA tree from its root
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet. 2012 May 4;90(5):936
Abstract
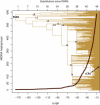
Mutational events along the human mtDNA phylogeny are traditionally identified relative to the revised Cambridge Reference Sequence, a contemporary European sequence published in 1981. This historical choice is a continuous source of inconsistencies, misinterpretations, and errors in medical, forensic, and population genetic studies. Here, after having refined the human mtDNA phylogeny to an unprecedented level by adding information from 8,216 modern mitogenomes, we propose switching the reference to a Reconstructed Sapiens Reference Sequence, which was identified by considering all available mitogenomes from Homo neanderthalensis. This "Copernican" reassessment of the human mtDNA tree from its deepest root should resolve previous problems and will have a substantial practical and educational influence on the scientific and public perception of human evolution by clarifying the core principles of common ancestry for extant descendants.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
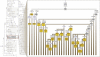
References
-
- Darwin C. John Murray; London: 1859. Natural Selection. On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or, The Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life, Chapter 4. - PubMed
-
- Delsuc F., Brinkmann H., Philippe H. Phylogenomics and the reconstruction of the tree of life. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:361–375. - PubMed
-
- Kivisild T., Metspalu E., Bandelt H.J., Richards M., Villems R. The world mtDNA phylogeny. In: Bandelt H.J., Macaulay V., Richards M., editors. Human mitochondrial DNA and the evolution of Homo sapiens. Springer-Verlag; Berlin: 2006. pp. 149–179.
-
- Ingman M., Kaessmann H., Pääbo S., Gyllensten U. Mitochondrial genome variation and the origin of modern humans. Nature. 2000;408:708–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

