Inhibition of ARNT severely compromises endothelial cell viability and function in response to moderate hypoxia
- PMID: 22484908
- PMCID: PMC3661274
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-012-9269-x
Inhibition of ARNT severely compromises endothelial cell viability and function in response to moderate hypoxia
Abstract
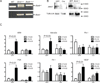
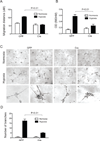
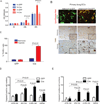
Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) is a master heterodimeric transcriptional regulator of oxygen (O(2)) homeostasis critical to proper angiogenic responses. Due to the distinctive coexpression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α subunits in endothelial cells, our goal was to examine the genetic elimination of HIF transcriptional activity in response to physiological hypoxic conditions by using a genetic model in which the required HIF-β subunit (ARNT, Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor Nuclear Translocator) to HIF transcriptional responses was depleted. Endothelial cells (ECs) and aortic explants were isolated from Arnt ( loxP/loxP ) mice and infected with Adenovirus-Cre/GFP or control-GFP. We observed that moderate levels of 2.5 % O(2) promoted vessel sprouting, growth, and branching in control aortic ring assays while growth from Adenovirus-Cre infected explants was compromised. Primary Adenovirus-Cre infected EC cultures featured adverse migration and tube formation phenotypes. Primary pulmonary or cardiac ARNT-deleted ECs also failed to proliferate and survive in response to 8 or 2.5 % O(2) and hydrogen peroxide treatment. Our data demonstrates that ARNT promotes EC migration and vessel outgrowth and is indispensible for the proliferation and preservation of ECs in response to the physiological environmental cue of hypoxia. Thus, these results demonstrate that ARNT plays a critical intrinsic role in ECs and support an important collaboration between HIF-1 and HIF-2 transcriptional activity in these cells.
Figures

References
-
- Cockman ME, Masson N, Mole DR, Jaakkola P, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Maher ER, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Maxwell PH. Hypoxia inducible factor-alpha binding and ubiquitylation by the von hippel-lindau tumor suppressor protein. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(33):25733–25741. - PubMed
-
- Epstein JM, Gleadle AC, McNeill LA, Hewitson KS, O'Rourke J, Mole DR, Mukherji M, Metzen E, Wilson MI, Dhanda A, Tian YM, Masson N, Hamilton DL, Jaakkola P, Barstead R, Hodgkin J, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ. C. Elegans egl-9 and mammalian homologs define a family of dioxygenases that regulate hif by prolyl hydroxylation. Cell. 2001;107(1):43–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

