Alternative molecular tests for virological diagnosis
- PMID: 22484997
- PMCID: PMC7091206
- DOI: 10.1007/s12033-012-9533-8
Alternative molecular tests for virological diagnosis
Abstract
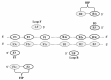
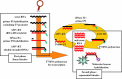
Several nucleic acid amplification techniques (NAATs), particularly PCR and real-time PCR, are currently used in the routine clinical laboratories. Such approaches have allowed rapid diagnosis with a high degree of sensitivity and specificity. However, conventional PCR methods have several intrinsic disadvantages such as the requirement for temperature cycling apparatus, and sophisticated and costly analytical equipments. Therefore, amplification at a constant temperature is an attractive alternative method to avoid these requirements. A new generation of isothermal amplification techniques are gaining a wide popularity as diagnostic tools due to their simple operation, rapid reaction and easy detection. The main isothermal methods reviewed here include loop-mediated isothermal amplification, nucleic acid sequence-based amplification, and helicase-dependent amplification. In this review, design criteria, potential of amplification, and application of these alternative molecular tests will be discussed and compared to conventional NAATs.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

