Enhanced delivery of chemotherapy to tumors using a multicomponent nanochain with radio-frequency-tunable drug release
- PMID: 22486623
- PMCID: PMC3358486
- DOI: 10.1021/nn300652p
Enhanced delivery of chemotherapy to tumors using a multicomponent nanochain with radio-frequency-tunable drug release
Abstract
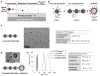
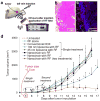
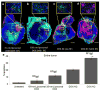
While nanoparticles maximize the amount of chemotherapeutic drug in tumors relative to normal tissues, nanoparticle-based drugs are not accessible to the majority of cancer cells because nanoparticles display patchy, near-perivascular accumulation in tumors. To overcome the limitations of current drugs in their molecular or nanoparticle form, we developed a nanoparticle based on multicomponent nanochains to deliver drug to the majority of cancer cells throughout a tumor while reducing off-target delivery. The nanoparticle is composed of three magnetic nanospheres and one doxorubicin-loaded liposome assembled in a 100 nm long chain. These nanoparticles display prolonged blood circulation and significant intratumoral deposition in tumor models in rodents. Furthermore, the magnetic particles of the chains serve as a mechanical transducer to transfer radio frequency energy to the drug-loaded liposome. The defects on the liposomal walls trigger the release of free drug capable of spreading throughout the entire tumor, which results in a widespread anticancer effect.
Figures




References
-
- Von Hoff DD, Layard MW, Basa P, Davis HL, Jr, Von Hoff AL, Rozencweig M, Muggia FM. Risk Factors for Doxorubicin-Induced Congestive Heart Failure. Ann Intern Med. 1979;91:710–717. - PubMed
-
- Maeda H, Wu J, Sawa T, Matsumura Y, Hori K. Tumor Vascular Permeability and the EPR Effect in Macromolecular Therapeutics: A Review. J Control Release. 2000;65:271–284. - PubMed
-
- Lasic DD. Doxorubicin in Sterically Stabilized Liposomes. Nature. 1996;380:561–562. - PubMed
-
- Dreher MR, Liu W, Michelich CR, Dewhirst MW, Yuan F, Chilkoti A. Tumor Vascular Permeability, Accumulation, and Penetration of Macromolecular Drug Carriers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:335–344. - PubMed
-
- Yuan F. Transvascular Drug Delivery in Solid Tumors. Semin Radiat Oncol. 1998;8:164–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

