Population pharmacokinetics of clindamycin orally and intravenously administered in patients with osteomyelitis
- PMID: 22486719
- PMCID: PMC3522810
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04292.x
Population pharmacokinetics of clindamycin orally and intravenously administered in patients with osteomyelitis
Abstract
Aims: This study was performed to describe clindamycin, administered either orally or intravenously, concentration-time courses to patients with osteomyelitis, to study the effects of different covariates on clindamycin pharmacokinetics and to simulate an optimized administration scheme.
Methods: Clindamycin concentrations were measured in 50 patients. A total of 122 plasma concentrations were available (58 from oral administration and 64 from i.v. infusion). A population pharmacokinetic model was developed with MONOLIX 4 software.
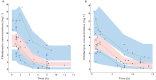
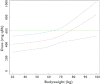
Results: A one compartment model adequately described the data. Clindamycin clearance increased significantly with body weight (BW). The typical population estimates (interindividual variability) for clearance, volume of distribution and absorption rate constant were 16.2 l h(-1) (0.39), 70.2 l and 0.92 h(-1) , respectively. The bioavailability of the oral form was estimated to be 87.6%. According to BW, theoretical doses needed to reach a C(min) of 2 mg l(-1) were then calculated.
Conclusions: The current recommendation of 600 mg three times daily seems to be effective up to 75 kg but the dose should be raised to 900 mg three times daily thereafter. These assumptions should be prospectively confirmed.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Lazzarini L, Lalla F, de, Mader JT. Long bone osteomyelitis. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2002;4:439–45. - PubMed
-
- Lazzarini L, Lipsky BA, Mader JT. Antibiotic treatment of osteomyelitis: what have we learned from 30 years of clinical trials? Int J Infect Dis. 2005;9:127–38. - PubMed
-
- Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 5th edn. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone; 2000. on CD-ROM. 5th éd.
-
- Dornbusch K, Carlström A, Hugo H, Lidströlm A. Antibacterial activity of clindamycin and lincomycin in human bone. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977;3:153–60. - PubMed
-
- Panzer JD, Brown DC, Epstein WL, Lipson RL, Mahaffey HW, Atkinson WH. Clindamycin levels in various body tissues and fluids. J Clin Pharmacol. 1972;12:259–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

